About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1253 results
Modeling Asian-Papuan Admixture during the Neolithic Expansion across Island Southeast Asia
Murray Cox François Vallée | Published Friday, December 09, 2016This Repast Simphony model simulates genomic admixture during the farming expansion of human groups from mainland Asia into the Papuan dominated islands of Southeast Asia during the Neolithic period.
Peer reviewed FishCensus
Miguel Pais | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, February 09, 2017The FishCensus model simulates underwater visual census methods, where a diver estimates the abundance of fish. A separate model is used to shape species behaviours and save them to a file that can be shared and used by the counting model.
Individual time preferences and adoption of destructive extraction methods
Marco Janssen Aneeque Javaid Hauke Reuter Achim Schlueter | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2016We model the relationship between natural resource user´s individual time preferences and their use of destructive extraction method in the context of small-scale fisheries.
Interplay of actors about the construction of a dam
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc | Published Monday, December 05, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, May 09, 2018Model of a very serious conflict about the relevance of a dam to impede its construction, between the client, the prime contractor, State, legalist opponents and activist opponents.
TREELIM
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Wednesday, November 30, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 10, 2017The model simulates the spatial patterns of secondary forest succession above the current alpine tree line in the context of land use and climate change. Three scenarios are offered: (1) climate change, (2) land use change, (3) species composition.
ForagerNet3_Demography_V3
Andrew White | Published Tuesday, November 29, 2016The ForagerNet3_Demography model is a non-spatial ABM designed to serve as a platform for exploring several aspects of hunter-gatherer demography.
HomininSpace
Fulco Scherjon | Published Friday, November 25, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, October 06, 2020A modelling system to simulate Neanderthal demography and distribution in a reconstructed Western Europe for the late Middle Paleolithic.
LimnoSES - social-ecological lake management undergoing regime shifts
Romina Martin | Published Thursday, November 24, 2016 | Last modified Friday, January 18, 2019LimnoSES is a coupled system dynamics, agent-based model to simulate social-ecological feedbacks in shallow lake use and management.
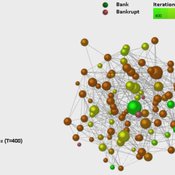
Dynamic Interbank Network Simulator
Valentina Guleva | Published Wednesday, November 23, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 13, 2020The model provides instruments for the simulation of interbank network evolution. There are tools for dynamic network analysis, allowing to evaluate graph topological invariants, thermodynamic network features and combinational node-based features.
Growing Unpopular Norms. A Network-Situated ABM of Norm Choice.
C Merdes | Published Tuesday, November 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, March 17, 2018The model’s purpose is to provide a potential explanation for the emergence, sustenance and decline of unpopular norms based on pluralistic ignorance on a social network.
Displaying 10 of 1253 results