About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1253 results
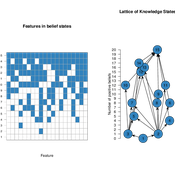
Knowledge Space Model for Opinion Dynamics
Shane Mueller | Published Thursday, September 28, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, September 20, 2018Knowledge Space model of Opinion Dynamics.
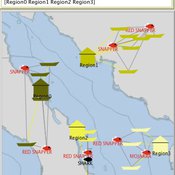
The Mobility Model
Emilie Lindkvist | Published Wednesday, September 27, 2017 | Last modified Friday, October 06, 2017The Mobility Model is a model of a small-scale fishery with the purpose to study the movement of fishers between different sub-regions within a larger region, as they move between different regions to fish.
Modeling a Victim-Centered Approach for Detection of Human Trafficking Victims within Migration Flows
Kyle Ballard Brant M Horio | Published Saturday, September 23, 2017The model employs an agent-based model for exploring the victim-centered approach to identifying human trafficking and the approach’s effectiveness in an abstract representation of migrant flows.
Zero, Some, or Zero-Sum: Exploring Trade-Offs in Identifying Human Trafficking Among Migration Flows
Kyle Ballard | Published Saturday, September 23, 2017The model attempts to explore the trade-offs between immigration policies and successfully identifying human trafficking victims.
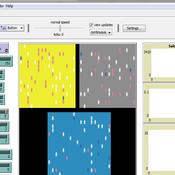
Lakeland 2 is a simple version of the original Lakeland of Jager et al. (2000) Ecological Economics 35(3): 357-380. The model can be used to explore the consequences of different behavioral assumptions on resource and social dynamics.
Impact of topography and climate change on Magdalenian social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Monday, September 11, 2017The model presented here was created as part of my dissertation. It aims to study the impacts of topography and climate change on prehistoric networks, with a focus on the Magdalenian, which is dated to between 20 and 14,000 years ago.
Sorghum supply development in Meru County, Kenya
Tim Verwaart Coen Van Wagenberg | Published Wednesday, September 06, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, May 30, 2019Trust between farmers and processors is a key factor in developing stable supply chains including “bottom of the pyramid”, small-scale farmers. This simulation studies a case with 10000 farmers.
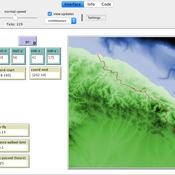
Peer reviewed Least cost path mobility
Colin Wren Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Saturday, September 02, 2017 | Last modified Monday, October 04, 2021This model aims to mimic human movement on a realistic topographical surface. The agent does not have a perfect knowledge of the whole surface, but rather evaluates the best path locally, at each step, thus mimicking imperfect human behavior.
Policy Formulation for Public Administration - Innovation
Bashar Ourabi | Published Tuesday, August 29, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, August 29, 2017Innovation a byproduct of the intellectual capital, requires a new paradigm for the production constituents. Human Capital HC,Structural capital SC and relational capital RC become key for intellectual capital and consequently for innovation.
InnovationGame
Madeline Tyson | Published Thursday, August 24, 2017This model includes an innovation search environment. Agents search and can share their findings. It’s implemented in Netlogo-Hubnet & a parallel Netlogo model. This allows for validation of search strategies against experimental findings.
Displaying 10 of 1253 results