About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 38 results for "Krzysztof Domino" clear search
Will you infect me with your opinion?
Jarosław Miszczak Krzysztof Domino | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2022 | Last modified Monday, August 29, 2022This model incorporates three mechanisms shaping the dynamics of opinion formation, which mimics the dynamics of the virus spreading in the population. There are three methods of getting infected (or convinced) - direct contact, indirect contact, and contact with ``contaminated’’ elements.
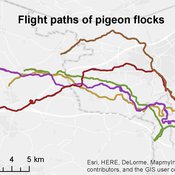
Homing pigeon model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016This model represents the flight paths of a flock of homing pigeons according to their flocking-, orientation- and leadership behaviour.
An adaptive model of homing pigeons: A genetic algorithm approach
Gudrun Wallentin Francis Oloo | Published Friday, January 27, 2017In this model, we simulate the navigation behavior of homing pigeons. Specifically we use genetic algorithms to optimize the navigation and flocking parameters of pigeon agents.
NetLogo-R-Example for the Inititialisation of Agents with Correlated Random Numbers
Danilo Saft | Published Friday, February 14, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This is a short NetLogo example demonstrating how to initialize 500 agents with 4 correlated parameters each with random values by doing the necessary calculations in the program “R” and retrieving the results.
ergodicity_test
Jakob Grazzini | Published Monday, November 29, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This Python module contain a function that is able to test the ergodicity of a given agent based model. It is sufficient to produce one long time series and many smaller time series. The function uses
Team Structure and Task Performance
Davide Secchi Martin Neumann | Published Monday, August 05, 2024This model was designed to study resilience in organizations. Inspired by ethnographic work, it follows the simple goal to understand whether team structure affects the way in which tasks are performed. In so doing, it compares the ‘hybrid’ data-inspired structure with three more traditional structures (i.e. hierarchy, flexible/relaxed hierarchy, and anarchy/disorganization).
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
CRESY-I stands for CREativity from a SYstems perspetive, Model I. This is the base model in a series designed to describe a systems approach to creativity in terms of variation, selection and retention (VSR) subprocesses.
FLOSSSim: An Agent-Based Model of the Free/Libre Open Source Software (FLOSS) Development Process
Nicholas Radtke | Published Saturday, December 31, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of the Free/Libre Open Source Software (FLOSS) development process designed around agents selecting FLOSS projects to contribute to and/or download.
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
Displaying 10 of 38 results for "Krzysztof Domino" clear search