About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1108 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search
One of four extensions to the standard Adder model that replicates the various interventions typically associated with transition experiments.
The fourth and final extension to the standard Adder model to replicate the various interventions typically associated with Transition Experiments.
Drafting agent-based modeling into basketball analytics
Matthew Oldham | Published Tuesday, February 19, 2019An agent-based simulation of a game of basketball. The model implements most components of a standard game of basketball. Additionally, the model allows the user to test for the effect of two separate cognitive biases – the hot-hand effect and a belief in the team’s franchise player.
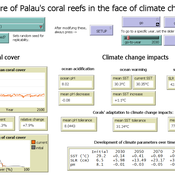
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
MoPAgrIB: simulating savannah landscape mosaic under shifting cultivation
Nicolas Becu Marc Deconchat Eric Garine Kouami Kokou Christine Raimond | Published Monday, May 27, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2014MoPAgrIB model simulates the movement of cultivated patches in a savannah vegetation mosaic ; how they move and relocate through the landscape, depending on farming practices, population growth, social rules and vegetation growth.
The model implements a model that reflects features of a rural hill village in Nepal. Key features of the model include water storage, social capital and migration of household members who then send remittances back to the village.
Agent-based Simulation Models of the College Sorting Process
Rachel Baker Sean F Reardon Matt Kasman Daniel Klasik | Published Friday, May 23, 2014We explore how dynamic processes related to socioeconomic inequality operate to sort students into, and create stratification among, colleges.
An agent-based model of cultural change for a low-carbon transition
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, November 10, 2023An ABM of changes in individuals’ lifestyles which considers their
evolving behavioural choices. Individuals have a set of environmental behavioural traits that spread through a fixed Watts–Strogatz graph via social interactions with their neighbours. These exchanges are mediated by transmission biases informing from whom an individual learns and
how much attention is paid. The influence of individuals on each other is a function of their similarity in environmental identity, where we represent environmental identity computationally by aggregating past agent attitudes towards multiple environmentally related behaviours. To perform a behaviour, agents must both have
a sufficiently positive attitude toward a behaviour and overcome a corresponding threshold. This threshold
structure, where the desire to perform a behaviour does not equal its enactment, allows for a lack of coherence
between attitudes and actual emissions. This leads to a disconnect between what people believe and what
…
Interplay of actors about the construction of a dam
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc | Published Monday, December 05, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, May 09, 2018Model of a very serious conflict about the relevance of a dam to impede its construction, between the client, the prime contractor, State, legalist opponents and activist opponents.
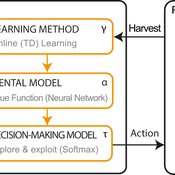
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
Displaying 10 of 1108 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search