About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1115 results for "Elena A. Pearce" clear search
Hedonic and Eudaimonic Well-being Based Reward for Intrinsic Motivated Reinforcement Learning Agents
Yue Gao Shimon Edelman | Published Monday, March 21, 2016The code contains four experiments for well-being based IMRL reward features.
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
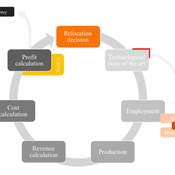
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
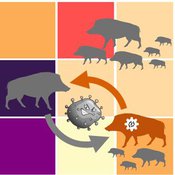
Classical Swine Fever in wild boars
Volker Grimm Stephanie Kramer-Schadt Cédric Scherer Martin Lange Hans-Hermann Thulke | Published Friday, September 06, 2019The model is a combination of a spatially explicit, stochastic, agent-based model for wild boars (Sus scrofa L.) and an epidemiological model for the Classical Swine Fever (CSF) virus infecting the wild boars.
The original model (Kramer-Schadt et al. 2009) was used to assess intrinsic (system immanent host-pathogen interaction and host life-history) and extrinsic (spatial extent and density) factors contributing to the long-term persistence of the disease and has further been used to assess the effects of intrinsic dynamics (Lange et al. 2012a) and indirect transmission (Lange et al. 2016) on the disease course. In an applied context, the model was used to test the efficiency of spatiotemporal vaccination regimes (Lange et al. 2012b) as well as the risk of disease spread in the country of Denmark (Alban et al. 2005).
References: See ODD model description.
Biodiversity and Adoption of Small-scale Agroforestry in Rwanda (BASAR)
Beatrice Nöldeke Etti Winter Elisée Bahati Ntawuhiganayo | Published Friday, July 15, 2022The BASAR model aims to investigate different approaches to describe small-scale farmers’ decision-making in the context of diversified agroforestry adoption in rural Rwanda. Thereby, it compares random behaviour with perfect rationality (non-discounted and discounted utility maximization), bounded rationality (satisficing and fast and frugal decision tree heuristics), Theory of Planned Behaviour, and a probabilistic regression-based approach. It is aimed at policy-makers, extension agents, and cooperatives to better understand how rural farmers decide about implementing innovative agricultural practices such as agroforestry and at modelers to support them in selecting an approach to represent human decision-making in ABMs of Social-Ecological Systems. The overall objective is to identify a suitable approach to describe human decision-making and therefore improve forecasts of adoption rates and support the development and implementation of interventions that aim to raise low adoption rates.
The Epistemic Role of Diversity in Juries
Aaron Bramson Patrick Grim Daniel J Singer Jiin Jung William J. Berger Bennett Holman | Published Wednesday, August 16, 2023This model is linked to the paper “The Epistemic Role of Diversity in Juries: An Agent-Based Model”. There are many version of this model, but the current version focuses on the role of diversity in whether juries reach correct verdicts. Using this agent-based model, we argue that diversity can play at least four importantly different roles in affecting jury verdicts. (1) Where different subgroups have access to different information, equal representation can strengthen epistemic jury success. (2) If one subgroup has access to particularly strong evidence, epistemic success may demand participation by that group. (3) Diversity can also reduce the redundancy of the information on which a jury focuses, which can have a positive impact. (4) Finally, and most surprisingly, we show that limiting communication between diverse groups in juries can favor epistemic success as well.
Agent-based modeling of the spatio-temporal distribution of Sahelian transhumant herds
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Tuesday, May 20, 2025Sahelian transhumance is a seasonal pastoral mobility between the transhumant’s terroir of origin and one or more host terroirs. Sahelian transhumance can last several months and extend over hundreds of kilometers. Its purpose is to ensure efficient and inexpensive feeding of the herd’s ruminants. This paper describes an agent-based model to determine the spatio-temporal distribution of Sahelian transhumant herds and their impact on vegetation. Three scenarios based on different values of rainfall and the proportion of vegetation that can be grazed by transhumant herds are simulated. The results of the simulations show that the impact of Sahelian transhumant herds on vegetation is not significant and that rainfall does not impact the alley phase of transhumance. The beginning of the rainy season has a strong temporal impact on the spatial distribution of transhumant herds during the return phase of transhumance.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
Informal risk-sharing cooperatives : ORP and Learning
Juliette Rouchier Victorien Barbet Renaud Bourlès | Published Monday, February 13, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 16, 2023The model studies the dynamics of risk-sharing cooperatives among heterogeneous farmers. Based on their knowledge on their risk exposure and the performance of the cooperative farmers choose whether or not to remain in the risk-sharing agreement.
Agent-based model of WiFi tracking system in urban environment
Christopher Thron Khoi Tran | Published Friday, April 21, 2017This code simulates the WiFi user tracking system described in: Thron et al., “Design and Simulation of Sensor Networks for Tracking Wifi Users in Outdoor Urban Environments”. Testbenches used to create the figures in the paper are included.
Peer reviewed Agent-based model to simulate equilibria and regime shifts emerged in lake ecosystems
no contributors listed | Published Tuesday, January 25, 2022(An empty output folder named “NETLOGOexperiment” in the same location with the LAKEOBS_MIX.nlogo file is required before the model can be run properly)
The model is motivated by regime shifts (i.e. abrupt and persistent transition) revealed in the previous paleoecological study of Taibai Lake. The aim of this model is to improve a general understanding of the mechanism of emergent nonlinear shifts in complex systems. Prelimnary calibration and validation is done against survey data in MLYB lakes. Dynamic population changes of function groups can be simulated and observed on the Netlogo interface.
Main functional groups in lake ecosystems were modelled as super-individuals in a space where they interact with each other. They are phytoplankton, zooplankton, submerged macrophyte, planktivorous fish, herbivorous fish and piscivorous fish. The relationships between these functional groups include predation (e.g. zooplankton-phytoplankton), competition (phytoplankton-macrophyte) and protection (macrophyte-zooplankton). Each individual has properties in size, mass, energy, and age as physiological variables and reproduce or die according to predefined criteria. A system dynamic model was integrated to simulate external drivers.
Set biological and environmental parameters using the green sliders first. If the data of simulation are to be logged, set “Logdata” as true and input the name of the file you want the spreadsheet(.csv) to be called. You will need create an empty folder called “NETLOGOexperiment” in the same level and location with the LAKEOBS_MIX.nlogo file. Press “setup” to initialise the system and “go” to start life cycles.
Displaying 10 of 1115 results for "Elena A. Pearce" clear search