About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1108 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search
CHAAHK: a Spatial Simulation of the Maya Elevated Core Region
Alex Kara | Published Tuesday, December 04, 2018 | Last modified Thursday, September 26, 2019This thesis presents an abstract spatial simulation model of the Maya Central Lowlands coupled human and natural system from 1000 BCE to the present day. It’s name is the Climatically Heightened but Anothropogenically Achieved Historical Kerplunk model (CHAAHK). The simulation features features virtual human groups, population centers, transit routes, local resources, and imported resources. Despite its embryonic state, the model demonstrates how certain anthropogenic characteristics of a landscape can interact with externally induced trauma and result in a prolonged period of relative sociopolitical uncomplexity. Analysis of batch simulation output suggests decreasing empirical uncertainties about ancient wetland modification warrants more investment. This first submission of CHAAHK’s code represents the simulation’s implementation that was featured in the author’s master’s thesis.
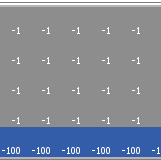
Cliff Walking with Q-Learning NetLogo Extension
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This model implements a classic scenario used in Reinforcement Learning problem, the “Cliff Walking Problem”. Consider the gridworld shown below (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018). This is a standard undiscounted, episodic task, with start and goal states, and the usual actions causing movement up, down, right, and left. Reward is -1 on all transitions except those into the region marked “The Cliff.” Stepping into this region incurs a reward of -100 and sends the agent instantly back to the start (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018).
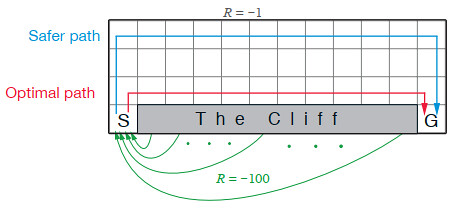
The problem is solved in this model using the Q-Learning algorithm. The algorithm is implemented with the support of the NetLogo Q-Learning Extension
An agent based model of a population subject to floods
Bruno Bonté Katrin Erdlenbruch | Published Wednesday, September 22, 2021This model allows simulating the impacts of floods on a population. Floods are described by their intensity (flood height) and date of occurrence. Households are more or less severely hit by floods according to their geographical situation. Impacts are measured in terms of reductions in household wealth. Households may take up protection measures against floods, depending on their individual characteristics, a social network and information campaigns. If such measures are taken, flood impacts (wealth reduction) are less severe. Information campaigns increase the probability that households adopt protection measures. Two types of information campaigns are modeled: top-down policies which are the same for all households, people-centered policies, which adapt to the individual characteristics of each household.
Agent-based Modeling of Evolving Intergovernmental Networks
Sungho Lee | Published Thursday, January 29, 2009 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This agent-based model using ‘Blanche’ software provides policy-makers with a simulation-based demonstration illustrating how autonomous agents network and operate complementary systems in a decentral
Evolution of cooperation via indirect reciprocity by image scoring
Marco Janssen | Published Friday, October 22, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model explores the possibility of the evolution of cooperation due to indirect reciprocity when agents derive information about the past behavior of the opponent in one-shot dilemma games.
COVID-19 US Masks
Dale Brearcliffe | Published Sunday, October 18, 2020This model is an abstract simulation of the COVID-19 virus in the United States population. It demonstrates how different masks of different types affect the progress of the virus.
Peer reviewed INOvPOP
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Wednesday, June 01, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, July 10, 2024INOvPOP is designed to simulate population dynamics (abundance, sex-age composition and distribution in the landscape) of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) for selected Indiana counties. Updated for netLogo 6.4.0
Firm explore-exploit of knowledge
Rosanna Garcia | Published Monday, March 28, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The basic premise of the model is to simulate several ‘agents’ going through build-buy cycles: Build: Factories follow simple rules of strategy in the allocation of resources between making exploration and exploitation type products. Buy: Each of two types of Consumers, early-adopters and late adopters, follow simple purchase decision rules in deciding to purchase a product from one of two randomly chosen factories. Thus, the two working ‘agents’ of the model are ‘factories’ and […]
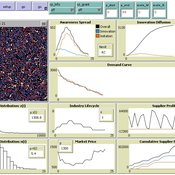
(Policy induced) Diffusion of Innovations - An integrated demand-supply Model based on Cournot Competition
Martin Rixin | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Objective is to simulate policy interventions in an integrated demand-supply model. The underlying demand function links both sides. Diffusion proceeds if interactions distribute awareness (Epidemic effect) and rivalry reduces the market price (Probit effect). Endogeneity is given due to the fact that consumer awareness as well as their willingness-to-pay drives supply-side rivalry. Firm´s entry and exit decisions as well as quantity and price settings are driven by Cournot competition.
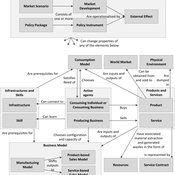
Generic servicising model (SPREE project)
Igor Nikolic Reinier Van Der Veen Kasper H Kisjes | Published Wednesday, August 26, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, September 28, 2016This generic agent-based model allows the user to simulate and explore the influence of servicising policies on the uptake of servicising and on economic, environmental and social effects, notably absolute decoupling.
Displaying 10 of 1108 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search