About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 988 results for "Rolf Anker Ims" clear search
Cultural Spread
Salvador Pardo Gordó Salvador Pardo-Gordó | Published Thursday, April 02, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 23, 2020The purpose of the model is to simulate the cultural hitchhiking hypothesis to explore how neutral cultural traits linked with advantageous traits spread together over time
Tail biting behaviour in pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans Iris Jmm Boumans | Published Friday, April 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 14, 2016The model simulates tail biting behaviour in pigs and how they can turn into a biter and/or victim. The effect of a redirected motivation, behavioural changes in victims and preference to bite a lying pig on tail biting can be tested in the model
Anxiety-to-Approach Agent-Based Model (Netlogo)
Marie Lisa Kogler | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2023An Agent-Based Model to simulate agent reactions to threatening information based on the anxiety-to-approach framework of Jonas et al. (2014).
The model showcases the framework of BIS/BAS (inhibitory and approach motivated behavior) for the case of climate information, including parameters for anxiety, environmental awareness, climate scepticism and pro-environmental behavior intention.
Agents receive external information according to threat-level and information frequency. The population dynamic is based on the learning from that information as well as social contagion mechanisms through a scale-free network topology.
The model uses Netlogo 6.2 and the network extension.
…
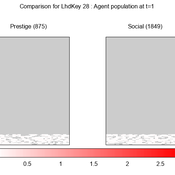
We provide a theory-grounded, socio-geographic agent-based model to present a possible explanation for human movement in the Adriatic region within the Cetina phenomenon.
Focusing on ideas of social capital theory from Piere Bordieu (1986), we implement agent mobility in an abstract geography based on cultural capital (prestige) and social capital (social position). Agents hold myopic representations of social (Schaff, 2016) and geographical networks and decide in a heuristic way on moving (and where) or staying.
The model is implemented in a fork of the Laboratory for Simulation Development (LSD), appended with GIS capabilities (Pereira et. al. 2020).
Simulation of Dual Information Exposure Networks: An Agent-Based Model of Panic Buying Behavior in China
dachenga | Published Thursday, April 11, 2024The main function of this simulation model is to simulate the onset of individual panic in the context of a public health event, and in particular to simulate how an individual’s panic develops and dies out in the context of a dual information contact network of online social media information and offline in-person perception information. In this model, eight different scenarios are set up by adjusting key parameters according to the difference in the amount and nature of information circulating in the dual information network, in order to observe how the agent’s panic behavior will change under different information exposure situations.
Peer reviewed Evolution of Conditional Cooperation in a Spatial Public Goods Game
Marco Janssen Francesca Federico Raksha Balakrishna | Published Saturday, March 15, 2025A model to investigate the Evolution of Conditional Cooperation in a Spatial Public Goods Game. We consider two conditional cooperation strategies: one based on thresholds (Battu & Srinivasan, 2020) and another based on independent decisions for each number of cooperating neighbors. We examine the effects of productivity and conditional cooperation criteria on the trajectory of cooperation. Cooperation is evolving with no need for additional mechanisms apart from spatial structure when agents follow conditional strategies. We confirm the positive influence of productivity and cluster formation on the evolution of cooperation in spatial models. Results are robust for the two types of conditional cooperation strategies.
Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) Simulation for Compact Urban Growth in Dublin: An Agent-Based Model in NetLogo
ajithvyas | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2025This agent-based model simulates the implementation of a Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) mechanism in a stylized urban environment inspired by Dublin. It explores how developer agents interact with land parcels under spatial zoning, conservation protections, and incentive-based policy rules. The model captures emergent outcomes such as compact growth, green and heritage zone preservation, and public cost-efficiency. Built in NetLogo, the model enables experimentation with variable FSI bonuses, developer behavior, and spatial alignment of sending/receiving zones. It is intended as a policy sandbox to test market-aligned planning tools under behavioral and spatial uncertainty.
Online Collaboration, Competing for Attention
M Manning | Published Wednesday, July 19, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, January 24, 2019This is a model of a community of online communities. Using mechanisms such as win-stay, lose-shift, and preferential attachment the model can reproduce similar patterns to those of the Stack Exchange network.
InnovationGame
Madeline Tyson | Published Thursday, August 24, 2017This model includes an innovation search environment. Agents search and can share their findings. It’s implemented in Netlogo-Hubnet & a parallel Netlogo model. This allows for validation of search strategies against experimental findings.
PercolationPrice
Koen Frenken Luis Izquierdo Paolo Zeppini | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, May 03, 2018This model simulate product diffusion on different social network structures.
Displaying 10 of 988 results for "Rolf Anker Ims" clear search