About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 111 results policy clear search
The Effects of Fiscal Targets in a Currency Union: a Multi-Country Agent Based-Stock Flow Consistent Model
Ermanno Catullo Alessandro Caiani Mauro Gallegati | Published Saturday, March 11, 2017We present an Agent-Based Stock Flow Consistent Multi-Country model of a Currency Union to analyze the impact of changes in the fiscal regimes that is permanent changes in the deficit-to-GDP targets that governments commit to comply.
Urban Sprawl and Income segregation with effect from income level and inequality
Nina Schwarz Cheng Guo Carsten M Buchmann | Published Tuesday, November 01, 2016 | Last modified Friday, May 26, 2017This is a stylized model based on Alonso’s model investigating the relationship between urban sprawl and income segregation.
Urban-Dynamics-2017
Hideyuki Nagai Setsuya Kurahashi | Published Thursday, October 06, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, October 06, 2016This model is designed for the paper of “Bustle Changes the City - Facility for Stopping off and Modeling Urban Dynamics -“. And all experimental results in the paper were implemented in this model.
Equity Constrained Dispatching Model of Emergency Medical Services
Sreekanth V K Ram Babu Roy | Published Thursday, September 08, 2016 | Last modified Monday, May 01, 2017Model for evaluating various ambulance dispatching policies of an equity constrained emergency medical services under bounded rationality.
Stylized agricultural land-use model for resilience exploration
Patrick Bitterman | Published Tuesday, June 14, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model is a highly stylized land use model in the Clear Creek Watershed in Eastern Iowa, designed to illustrate the construction of stability landscapes within resilience theory.
Agent-based model for centralized student admission process
Connie Wang Shu-Heng Chen Bin-Tzong Chi | Published Wednesday, November 04, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, March 06, 2019This model is to match students and schools using real-world student admission mechanisms. The mechanisms in this model are serial dictatorship, deferred acceptance, the Boston mechanism, Chinese Parallel, and the Taipei mechanism.
EthnoCultural Tag model (ECT)
Bruce Edmonds David Hales | Published Friday, October 16, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, May 09, 2018Captures interplay between fixed ethnic markers and culturally evolved tags in the evolution of cooperation and ethnocentrism. Agents evolve cultural tags, behavioural game strategies and in-group definitions. Ethnic markers are fixed.
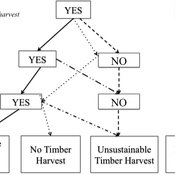
Private forest owner management behavior using social interactions, information flow, and peer-to-peer n
Jessica Leahy Emily Silver Huff Aaron R Weiskittel Caroline L Noblet David Hiebeler | Published Tuesday, October 13, 2015This theoretical model includes forested polygons and three types of agents: forest landowners, foresters, and peer leaders. Agent rules and characteristics were parameterized from existing literature and an empirical survey of forest landowners.
SimDrink: An agent-based NetLogo model of young, heavy drinkers for conducting alcohol policy experiments
Nick Scott James Wilson Michael Livingston Aaron Hart David Moore Paul Dietze | Published Friday, September 25, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, October 15, 2015A proof-of-concept agent-based model ‘SimDrink’, which simulates a population of 18-25 year old heavy alcohol drinkers on a night out in Melbourne to provide a means for conducting policy experiments to inform policy decisions.
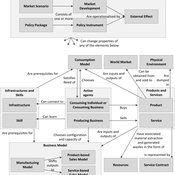
Generic servicising model (SPREE project)
Igor Nikolic Reinier Van Der Veen Kasper H Kisjes | Published Wednesday, August 26, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, September 28, 2016This generic agent-based model allows the user to simulate and explore the influence of servicising policies on the uptake of servicising and on economic, environmental and social effects, notably absolute decoupling.
Displaying 10 of 111 results policy clear search