About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 107 results for "Martijn de Vries" clear search
Game of Thrones model
Sean Bergin Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, January 03, 2021 | Last modified Sunday, January 03, 2021This model slowly evolves to become Westeros, with houses fighting for the thrones, and whitewalkers trying to kill all living things. You can download each version to see the evolution of the code, from the Wolf Sheep Predation model to the Game of Thrones model. If you are only interested in the end product, simply download the latest version.
For instructions on each step, see: https://claudinegravelmigu.wixsite.com/got-abm
Peninsula_Iberica 1.0
Carolina Cucart-Mora Sergi Lozano Javier Fernández-López De Pablo | Published Friday, November 04, 2016 | Last modified Monday, November 27, 2017This model was build to explore the bio-cultural interaction between AMH and Neanderthals during the Middle to Upper Paleolithic Transition in the Iberian Peninsula
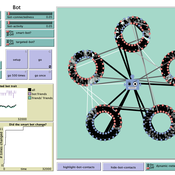
How do bots influence beliefs on social media? Why do beliefs propagated by social bots spread far and wide, yet does their direct influence appear to be limited?
This model extends Axelrod’s model for the dissemination of culture (1997), with a social bot agent–an agent who only sends information and cannot be influenced themselves. The basic network is a ring network with N agents connected to k nearest neighbors. The agents have a cultural profile with F features and Q traits per feature. When two agents interact, the sending agent sends the trait of a randomly chosen feature to the receiving agent, who adopts this trait with a probability equal to their similarity. To this network, we add a bot agents who is given a unique trait on the first feature and is connected to a proportion of the agents in the model equal to ‘bot-connectedness’. At each timestep, the bot is chosen to spread one of its traits to its neighbors with a probility equal to ‘bot-activity’.
The main finding in this model is that, generally, bot activity and bot connectedness are both negatively related to the success of the bot in spreading its unique message, in equilibrium. The mechanism is that very active and well connected bots quickly influence their direct contacts, who then grow too dissimilar from the bot’s indirect contacts to quickly, preventing indirect influence. A less active and less connected bot leaves more space for indirect influence to occur, and is therefore more successful in the long run.
Multi-agent model of the spread of climate change denial
Kalina Maria Piskorska Martin Takáč | Published Monday, March 03, 2025This NetLogo model simulates the spread of climate change beliefs within a population of individuals. Each believer has an initial belief level, which changes over time due to interactions with other individuals and exposure to media. The aim of the model is to identify possible methods for reducing climate change denial.
Peer reviewed Routes & Rumours 0.1.1
Jakub Bijak Martin Hinsch Oliver Reinhardt | Published Tuesday, July 12, 2022Routes & Rumours is an agent-based model of (forced) human migration. We model the formation of migration routes under the assumption that migrants have limited geographical knowledge concerning the transit area and rely to a large degree on information obtained from other migrants.
This is the final version of the model. To simulate the normative dynamics we used the EmIL (EMergence In the Loop) Framework which was kindly provided by Ulf Lotzmann. http://cfpm.org/EMIL-D5.1.pdf
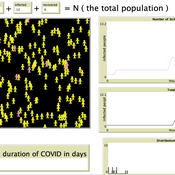
Introductory SIR Model
Kit Martin Amber Cesare Matthew Johnson | Published Tuesday, September 28, 2021This is a basic Susceptible, Infected, Recovered (SIR) model. This model explores the spread of disease in a space. In particular, it explores how changing assumptions about the number of susceptible people, starting number of infected people, as well as the disease’s infection probability, and average duration of infection. The model shows that the interactions of agents can drastically affect the results of the model.
We used it in our course on COVID-19: https://www.csats.psu.edu/science-of-covid19
COVID-19 SIR with Public Health Interventions
Kit Martin Amber Cesare Matthew Johnson | Published Tuesday, September 28, 2021This is an extension of the basic Suceptible, Infected, Recovered (SIR) model. This model explores the spread of disease in two spaces, one a treatment, and one a control. Through the modeling options, one can explore how changing assumptions about the number of susceptible people, starting number of infected people, the disease’s infection probability, and average duration impacts the outcome. In addition, this version allows users to explore how public health interventions like social distancing, masking, and isolation can affect the number of people infected. The model shows that the interactions of agents, and the interventions can drastically affect the results of the model.
We used the model in our course about COVID-19: https://www.csats.psu.edu/science-of-covid19
Peer reviewed PPHPC - Predator-Prey for High-Performance Computing
Nuno Fachada | Published Saturday, August 08, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, November 25, 2015PPHPC is a conceptual model for studying and evaluating implementation strategies for spatial agent-based models (SABMs). It is a realization of a predator-prey dynamic system, and captures important SABMs characteristics.
A model on feeding and social interaction behaviour of pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans | Published Thursday, May 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, February 27, 2018The model simulates interaction between internal physiological factors (e.g. energy balance) and external social factors (e.g. competition level) underlying feeding and social interaction behaviour of commercially group-housed pigs.
Displaying 10 of 107 results for "Martijn de Vries" clear search