About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 983 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search
Peer reviewed A Neutral Model of Stone Raw Material Procurement
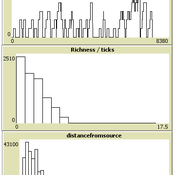
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013A simple model of random encounters of materials that produces distributions as found in the archaeological record.
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
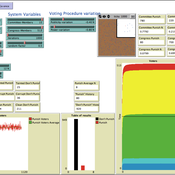
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Samambaia Basin - Hydro-ABM
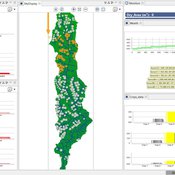
Pedro Phelipe Gonçalves Porto | Published Sunday, April 07, 2019 | Last modified Monday, May 06, 2019This model is a tool to support water management on Samambaia Basin. On it you can explore different scenarios of policy, management and externalities that could influence the water uses. (Scenarios already tested include less rain and payment on water use)
Sensitivity of the Deffuant model to measurement error
Dino Carpentras | Published Monday, June 07, 2021This code can be used to analyze the sensitivity of the Deffuant model to different measurement errors. Specifically to:
- Intrinsic stochastic error
- Binning of the measurement scale
- Random measurement noise
- Psychometric distortions
…
Agent-Based Computational Modeling of Cryptocurrency Design
Felix Ude | Published Friday, June 28, 2019Agent-Based Computational Model of the cryptocurrency Bitcoin with a realistic market and transaction system. Bitcoin’s transaction limit (i.e. block size) and Bitcoin generation can be calibrated and optimized for wealth and network’s hashing power by the Non-Dominated Sorted Genetic Algorithm - II.
Urban Dynamics
Hideyuki Nagai | Published Monday, November 11, 2019This is an urban dynamics ABM of abstraction of a city and residents’ activities there.
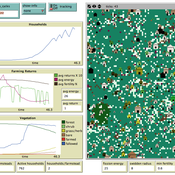
It allows you to evaluate the effects of urban policies, such as an introduction of an open facility for residents with pedestrian-friendly accommodations, promotion of bicycle use, and control of private automobile use in an urban central area, in controlling urban sprawl.
Peer reviewed Swidden Farming Version 2.0
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, June 12, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, September 03, 2014Model of shifting cultivation. All parameters can be controlled by the user or the model can be run in adaptive mode, in which agents innovate and select parameters.
Location Analysis Hybrid ABM
Lukasz Kowalski | Published Friday, February 08, 2019The purpose of this hybrid ABM is to answer the question: where is the best place for a new swimming pool in a region of Krakow (in Poland)?
The model is well described in ODD protocol, that can be found in the end of my article published in JASSS journal (available online: http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/22/1/1.html ). Comparison of this kind of models with spatial interaction ones, is presented in the article. Before developing the model for different purposes, area of interest or services, I recommend reading ODD protocol and the article.
I published two films on YouTube that present the model: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iFWG2Xv20Ss , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tDTtcscyTdI&t=1s
…
The cultural multiplier of climate policy
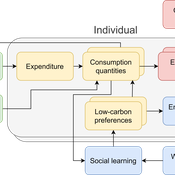
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Thursday, October 31, 2024For deep decarbonisation, the design of climate policy needs to account for consumption choices being influenced not only by pricing but also by social learning. This involves changes that pertain to the whole spectrum of consumption, possibly involving shifts in lifestyles. In this regard, it is crucial to consider not just short-term social learning processes but also slower, longer-term, cultural change. Against this background, we analyse the interaction between climate policy and cultural change, focusing on carbon taxation. We extend the notion of “social multiplier” of environmental policy derived in an earlier study to the context of multiple consumer needs while allowing for behavioural spillovers between these, giving rise to a “cultural multiplier”. We develop a model to assess how this cultural multiplier contributes to the effectiveness of carbon taxation. Our results show that the cultural multiplier stimulates greater low-carbon consumption compared to fixed preferences. The model results are of particular relevance for policy acceptance due to the cultural multiplier being most effective at low-carbon tax values, relative to a counter-case of short-term social interactions. Notably, at high carbon tax levels, the distinction between social and cultural multiplier effects diminishes, as the strong price signal drives even resistant individuals toward low-carbon consumption. By varying socio-economic conditions, such as substitutability between low- and high-carbon goods, social network structure, proximity of like-minded individuals and the richness of consumption lifestyles, the model provides insight into how cultural change can be leveraged to induce maximum effectiveness of climate policy.
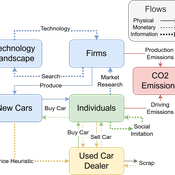
Driving in the wrong direction? A co-evolutionary model of electric vehicle adoption and innovation
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, July 11, 2025Car-centric societies face substantial challenges in moving towards sustainable
mobility systems, with internal combustion engine vehicles remaining a major
source of emissions. Electric vehicles play a critical role in addressing this challenge, yet their diffusion depends on the interaction of consumer behaviour, firm
innovation, and policy incentives. This paper develops an agent-based model to
examine these dynamics, calibrated on the data for the state of California over
2001-2023. In the model, heterogeneous car users influenced by their social peers
…
Displaying 10 of 983 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search