About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1110 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
Knowledge Sharing in a Hospital
bpint Emily Molfino Joshua Goldstein Kathryn Schaefer Ziemer Mark Orr Bryan Lewis Jose Jimenez | Published Friday, January 27, 2023Organizations are complex systems comprised of many dynamic and evolving interaction patterns among individuals and groups. Understanding these interactions and how patterns, such as informal structures and knowledge sharing behavior, emerge are crucial to creating effective and efficient organizations. To explore such organizational dynamics, the agent-based model integrates a cognitive model, dynamic social networks, and a physical environment.
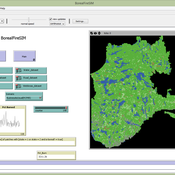
BorealFireSIM is a cellular automaton based model that serves to identify future fire patterns in the boreal forest of Quebec, Canada. The model simulates yearly fire seasons and adjusts decadal climate variables based on two future carbon pathways (RCP45 (low emissions) and RCP85 (business as usual)). The BorealFireSIM model simulates future fire patterns up to the year 2100.
COVID-19 ABM
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Tuesday, April 21, 2020Model of the Corona pandemic outbreak
The COVID-19 ABM aims to predict the qualitative behaviour of the CoViD-19 epidemic dynamics for the greater region of Salzburg City. Specifically, by means of scenario testing, it aims to help assessing how containment interventions can allow a stepwise relaxation of the lockdown without risking a new outbreak.
Virus Spread on Broad-degree-distribution Network.
Gianluca Manzo | Published Friday, July 24, 2020The model simulates the spread of a virus through a synthetic network with a degree distribution calibrated on close-range contact data. The model is used to study the macroscopic consequences of cross-individual variability in close-range contact frequencies and to assess whether this variability can be exploited for effective intervention targeting high-contact nodes.
A model of circular migration
Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, February 17, 2016An empirically validated agent-based model of circular migration
Peer reviewed Ache hunting
Kim Hill Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, August 13, 2013 | Last modified Friday, December 21, 2018Agent-based model of hunting behavior of Ache hunter-gatherers from Paraguay. We evaluate the effect of group size and cooperative hunting
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
Modeling the decline of labor-sharing in highly variable environments
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro | Published Tuesday, April 02, 2019The rapid environmental changes currently underway in many dry regions of the world, and the deep uncertainty about their consequences, underscore a critical challenge for sustainability: how to maintain cooperation that ensures the provision of natural resources when the benefits of cooperating are variable, sometimes uncertain, and often limited. We present an agent-based model that simulates the economic decisions of households to engage, or not, in labor-sharing agreements under different scenarios of water supply, water variability, and socio-environmental risk. We formulate the model to investigate the consequences of environmental variability on the fate of labor-sharing agreements between farmers. The economic decisions were implemented in the framework of prospect theory.
Lake Anderson Revisited II
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Monday, June 28, 2021The purpose of this study is another agent-based replication of a System Dynamics model (Anderson,1973) where he analysed the dynamics of nutrient, biomass, oxygen and detritus in a model lake under conditions of artificial fertilising and policies to deal with the consequences of artificial fertilising.. A first replication (Möhring & Troitzsch,2001) added those agents to the original model that were necessary to move the role of the experimenter into the model, whereas this replication replaces the original lake with a collection of small elements between which biomass, nurtrents and oxygen are exchanged, adds rivers upstream and downstream as well as adjacent land divided into villages and populated with farms and industrial plants run by individual persons.
Transitions between homophilic and heterophilic modes of cooperation
Genki Ichinose | Published Sunday, June 14, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, November 14, 2021In our model, individual agents are distributed over a two-dimensional square lattice. The agents play the prisoner’s dilemma game with their neighbors, imitate the highest strategy, and then migrate to empty sites based on their tag preference.
Displaying 10 of 1110 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search