About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search
Cyberworld 1
Dmitry Brizhinev Nathan Ryan Roger Bradbury | Published Thursday, April 23, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, February 25, 2018A Repast Simphony model of interactions (conflict and cooperation) between states
Diffusion of Innovations on Social Networks
Hang Xiong | Published Saturday, April 16, 2016This is model that simulates how multiple kinds of peer effects shape the diffusion of innovations through different types of social relationships.
Peer reviewed MIOvPOPsurveillance
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Monday, April 13, 2020MIOvPOPsurveillance is set up to simulate harvest-based chronic wasting disease (CWD) surveillance of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) populations in select Michigan Counties. New regions can be readily added, also the model can be readily adapted for other disease systems and used for informed-decision making during planning and implementation stages of disease surveillance in wildlife and free-ranging species.
Epidemic Simulation with Transportation Simulation
FG Econophysics FG Econophysics | Published Monday, March 01, 2021The Episim framework builds upon the established transportation simulation MATSim and is capable of tracking agents’ movements within a network and thus computing infection chains. Several characteristics of the virus and the environment can be parametred, whilst the infection dynamics is computed based upon a compartment model. The spread of the virus can be mitigated by restricting the agents’ activity in certain places.
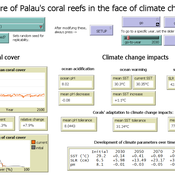
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Segregation and Opinion Polarization
Thomas Feliciani Andreas Flache Jochem Tolsma | Published Wednesday, April 13, 2016This is a tool to explore the effects of groups´ spatial segregation on the emergence of opinion polarization. It embeds two opinion formation models: a model of negative (and positive) social influence and a model of persuasive argument exchange.
Gender differentiation model
Sylvie Huet | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, April 23, 2020This is a gender differentiation model in terms of reputations, prestige and self-esteem (presented in the paper https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0236840). The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) considering two groups.
This agent-based model studies how inequalities can be explained by the difference of open-mindness between two groups of interacting agents. We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. We study an heterogeneous population of two different groups: one more open to influence of others, taking less into account their perceived difference of esteem, called L; a second one less prone to it, called S, who designed the credibility they give to others strongly based on how higher or lower valued than themselves they perceive them.
We show that a mixed population always turns in favor to some agents belonging to the group of less open-minded agents S, and harms the other group: (1) the average group self-opinion or reputation of S is always better than the one of L; (2) the higher rank in terms of reputation are more frequently occupied by the S agents while the L agents occupy more the bottom rank; (3) the properties of the dynamics of differentiation between the two groups are similar to the properties of the glass ceiling effect proposed by Cotter et al (2001).
Dynamic Interbank Network Simulator
Valentina Guleva | Published Wednesday, November 23, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 13, 2020The model provides instruments for the simulation of interbank network evolution. There are tools for dynamic network analysis, allowing to evaluate graph topological invariants, thermodynamic network features and combinational node-based features.
SBH trust model
Di Wang | Published Tuesday, December 14, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a computational model to articulate the theory and test some assumption and axioms for the trust model and its relationship to SBH.
The Informational Dynamics of Regime Change
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Saturday, October 07, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, January 14, 2020We model the epistemic dynamics preceding political uprising. Before deciding whether to start protests, agents need to estimate the amount of discontent with the regime. This model simulates the dynamics of group knowledge about general discontent.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search