About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 990 results for "Chantal van Esch" clear search
An integrated socio-economic Agent-Based Modeling framework towards assessing farmers’ decision making under water scarcity and varying utility function
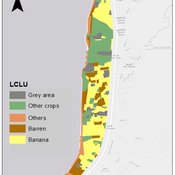
Ghinwa Harik | Published Tuesday, September 13, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, November 23, 2022A spatio-temporal Agent Based Modeling (ABM) framework is developed to probabilistically predict farmers’ decisions in the context of climate-induced water scarcity under varying utility optimization functions. The proposed framework forecasts farmers’ behavior assuming varying utility functions. The framework allows decision makers to forecast the behavior of farmers through a user-friendly platform with clear output visualization. The functionality of the proposed ABM is illustrated in an agriculturally dominated plain along the Eastern Mediterranean coastline.
Study area GIS data available upon request to gxh00@mail.aub.edu
Protein 2.0: An Agent-Based Model for Simulating Norway’s Protein Sector Under Carbon Pricing and the Emergence of Cultivated Proteins
Gary Polhill Nick Roxburgh Rob J.F. Burton Klaus Mittenzwei | Published Thursday, May 08, 2025Protein 2.0 is a systems model of the Norwegian protein sector designed to explore the potential impacts of carbon taxation and the emergence of cultivated meat and dairy technologies. The model simulates production, pricing, and consumption dynamics across conventional and cultivated protein sources, accounting for emissions intensity, technological learning, economies of scale, and agent behaviour. It assesses how carbon pricing could alter the competitiveness of conventional beef, lamb, pork, chicken, milk, and egg production relative to emerging cultivated alternatives, and evaluates the implications for domestic production, emissions, and food system resilience. The model provides a flexible platform for exploring policy scenarios and transition pathways in protein supply. Further details can be found in the associated publication.
An agent-based model of the journey of victim/survivors through local authority domestic abuse support services in the UK
Bruce Edmonds | Published Monday, July 28, 2025This model played a small part in the UK government’s review of the working of local authority implementation of the Domestic Abuse legislation. The model explicitly represents victim-survivor families as they: (a) try to contact the local DA support system, (b) are triaged by the system and (if there is space) allocated to safe temporary accomodation (c) recieve support services from this position and (d) eventually move on to more permenant accomodation. The purpose of the model was to understand some possible ways in which the implementation of DA Duty, might be frustrated in practice, the identification of gaps in the evidence base and to inform the developing Theory of Change. The key measures used for assessing outcomes in the model were the number of families helped and the services that were delivered to them. The exploration was grounded for in two archetypal cases: that of a relatively immature system for the delivery of DA services and a more mature one (based on actual local authority cases, but not based on any single one). See the official report under associated publications for a summary of results.
The Thin Blue Line Between Protesters and Their Counter-Protesters
Tamsin Lee | Published Monday, March 26, 2018More frequently protests are accompanied by an opposing group performing a counter protest. This phenomenon can increase tension such that police must try to keep the two groups separated. However, what is the best strategy for police? This paper uses a simple agent-based model to determine the best strategy for keeping the two groups separated. The ‘thin blue line’ varies in density (number of police), width and the keenness of police to approach protesters. Three different groups of protesters are modelled to mimic peaceful, average and volatile protests. In most cases, a few police forming a single-file ‘thin blue line’ separating the groups is very effective. However, when the protests are more volatile, it is more effective to have many police occupying a wide ‘thin blue line’, and police being keen to approach protesters. To the authors knowledge, this is the first paper to model protests and counter-protests.
Peer reviewed Circular Business Model experimentation: local biodigestion network
Igor Nikolic Kasper Pieter Hendrik Lange Gijsbert Korevaar Paulien Herder | Published Thursday, December 17, 2020 | Last modified Tuesday, June 29, 2021The purpose of the model is to explore the influence of the design of circular business models (CBMs) on CBM viability. The model represents an Industrial Symbiosis Network (ISN) in which a processor uses the organic waste from suppliers to produce biogas and nutrient rich digestate for local reuse. CBM viability is expressed as value captured (e.g., cash flow/tonne waste/agent) and the survival of the network over time (shown in the interface).
In the model, the value captured is calculated relative to the initial state, using incineration costs as a benchmark. Moderating variables are interactions with the waste incinerator and actor behaviour factors. Actors may leave the network when the waste supply for local production is too low, or when personal economic benefits are too low. When the processor decides to leave, the network fails. Theory of planned behaviour can be used to include agent behaviour in the simulations.
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
EMMIT (Extendable Model for Malaria Intervention Testing)
Jacob Heintzelman Greg R Madey | Published Thursday, May 27, 2021EMMIT is an end-user developed agent-based simulation of malaria transmission. The simulation’s development is a case study demonstrating an approach for non-technical investigators to easily develop useful simulations of complex public health problems. We focused on malaria transmission, a major global public health problem, and insecticide resistance (IR), a major problem affecting malaria control. Insecticides are used to reduce transmission of malaria caused by the Plasmodium parasite that is spread by the Anopheles mosquito. However, the emergence and spread of IR in a mosquito population can diminish the insecticide’s effectiveness. IR results from mutations that produce behavioral changes or biochemical changes (such as detoxification enhancement, target site alterations) in the mosquito population that provide resistance to the insecticide. Evolutionary selection for the IR traits reduces the effectiveness of an insecticide favoring the resistant mosquito population. It has been suggested that biopesticides, and specifically those that are Late Life Acting (LLA), could address this problem. LLA insecticides exploit Plasmodium’s approximate 10-day extrinsic incubation period in the mosquito vector, a delay that limits malaria transmission to older infected mosquitoes. Since the proposed LLA insecticide delays mosquito death until after the exposed mosquito has a chance to produce several broods of offspring, reducing the selective pressure for resistance, it delays IR development and gives the insecticide longer effectivity. Such insecticides are designed to slow the evolution of IR thus maintaining their effectiveness for malaria control. For the IR problem, EMMIT shows that an LLA insecticide could work as intended, but its operational characteristics are critical, primarily the mean-time-to-death after exposure and the associated standard deviation. We also demonstrate the simulation’s extensibility to other malaria control measures, including larval source control and policies to mitigate the spread of IR. The simulation was developed using NetLogo as a case study of a simple but useful approach to public health research.
Mast seeding model
Giangiacomo Bravo Lucia Tamburino | Published Saturday, September 08, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Purpose of the model is to perform a “virtual experiment” to test the predator satiation hypothesis, advanced in literature to explain the mast seeding phenomenon.
The model implements a model that reflects features of a rural hill village in Nepal. Key features of the model include water storage, social capital and migration of household members who then send remittances back to the village.
A simple model that aims to demonstrate the influence of agri-environmental payments on land-use patterns in a virtual landscape. The landscape consists of grassland (which can be managed extensively or intensively) and a river. Agri-environmental payments are provided for extensive management of grassland. Additionally, there are boni for (a) extensive grassland in proximity of the river; and (b) clusters (“agglomerations”) of extensive grassland. The farmers, who own randomly distributed grassland patches, make decisions either on the basis of simple income maximization or they maximize only up to an income threshold beyond which they seize making changes in management. The resulting landscape pattern is evaluated by means of three simple models for (a) agricultural yield, (b) habitat/biodiversity and (c) water quality. The latter two correspond to the two boni. The model has been developed within a small project called Aligning Agent-Based Modelling with Multi-Objective Land-Use Allocation (ALABAMA).
Displaying 10 of 990 results for "Chantal van Esch" clear search