About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 119 results for "Ryan Long" clear search
MUGS - Model of Urban Green Spaces
Stefano Picascia | Published Friday, September 17, 2021Abstract model investigating the determinants of inter- and intra-urban inequality in contact with nature. We explore the plausibility of a social integration hypothesis - whereby the primary factor in decisions to visit Urban Green Spaces (UGS) is an assessment of who else is likely to be using the space at the same time, and the assessment runs predominantly along class lines. The model simulates four cities in Scotland and shows the conditions under which the mechanisms theorised are sufficient to reproduce observed inequalities in UGS usage.
An integrated socio-economic Agent-Based Modeling framework towards assessing farmers’ decision making under water scarcity and varying utility function
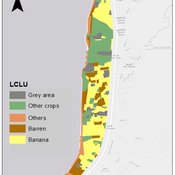
Ghinwa Harik | Published Tuesday, September 13, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, November 23, 2022A spatio-temporal Agent Based Modeling (ABM) framework is developed to probabilistically predict farmers’ decisions in the context of climate-induced water scarcity under varying utility optimization functions. The proposed framework forecasts farmers’ behavior assuming varying utility functions. The framework allows decision makers to forecast the behavior of farmers through a user-friendly platform with clear output visualization. The functionality of the proposed ABM is illustrated in an agriculturally dominated plain along the Eastern Mediterranean coastline.
Study area GIS data available upon request to gxh00@mail.aub.edu
Hohokam Water Management Simulation (HWM)
John Murphy | Published Wednesday, August 31, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Simulation of irrigation system management using archaeological data from southern Arizona
Peer reviewed Casting: A Bio-Inspired Method for Restructuring Machine Learning Ensembles
Colin Lynch Bryan Daniels | Published Thursday, September 18, 2025The wisdom of the crowd refers to the phenomenon in which a group of individuals, each making independent decisions, can collectively arrive at highly accurate solutions—often more accurate than any individual within the group. This principle relies heavily on independence: if individual opinions are unbiased and uncorrelated, their errors tend to cancel out when averaged, reducing overall bias. However, in real-world social networks, individuals are often influenced by their neighbors, introducing correlations between decisions. Such social influence can amplify biases, disrupting the benefits of independent voting. This trade-off between independence and interdependence has striking parallels to ensemble learning methods in machine learning. Bagging (bootstrap aggregating) improves classification performance by combining independently trained weak learners, reducing bias. Boosting, on the other hand, explicitly introduces sequential dependence among learners, where each learner focuses on correcting the errors of its predecessors. This process can reinforce biases present in the data even if it reduces variance. Here, we introduce a new meta-algorithm, casting, which captures this biological and computational trade-off. Casting forms partially connected groups (“castes”) of weak learners that are internally linked through boosting, while the castes themselves remain independent and are aggregated using bagging. This creates a continuum between full independence (i.e., bagging) and full dependence (i.e., boosting). This method allows for the testing of model capabilities across values of the hyperparameter which controls connectedness. We specifically investigate classification tasks, but the method can be used for regression tasks as well. Ultimately, casting can provide insights for how real systems contend with classification problems.
TERRoir level Organic matter Interactions and Recycling model
Myriam Grillot | Published Wednesday, April 19, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, June 17, 2020The TERROIR agent-based model was built for the multi-level analysis of biomass and nutrient flows within agro-sylvo-pastoral villages in West Africa. It explicitly takes into account both human organization and spatial extension of such flows.
Peer reviewed Viable North Sea (ViNoS): A NetLogo Agent-based Model of German Small-scale Fisheries
Wolfgang Nikolaus Probst Jieun Seo Jürgen Scheffran Carsten Lemmen Sascha Hokamp Verena Mühlberger Serra Örey | Published Thursday, May 25, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 05, 2023Viable North Sea (ViNoS) is an Agent-based Model of the German North Sea Small-scale Fisheries in a Social-Ecological Systems framework focussing on the adaptive behaviour of fishers facing regulatory, economic, and resource changes. Small-scale fisheries are an important part both of the cultural perception of the German North Sea coast and of its fishing industry. These fisheries are typically family-run operations that use smaller boats and traditional fishing methods to catch a variety of bottom-dwelling species, including plaice, sole, and brown shrimp. Fisheries in the North Sea face area competition with other uses of the sea – long practiced ones like shipping, gas exploration and sand extractions, and currently increasing ones like marine protection and offshore wind farming. German authorities have just released a new maritime spatial plan implementing the need for 30% of protection areas demanded by the United Nations High Seas Treaty and aiming at up to 70 GW of offshore wind power generation by 2045. Fisheries in the North Sea also have to adjust to the northward migration of their established resources following the climate heating of the water. And they have to re-evaluate their economic balance by figuring in the foreseeable rise in oil price and the need for re-investing into their aged fleet.
Gender Disparity in COVID-19’s Impact on Academic Careers: An Agent-Based Model
S.R. Aurora (a.k.a. Mai P. Trinh) Chantal van Esch | Published Tuesday, September 26, 2023Prior to COVID-19, female academics accounted for 45% of assistant professors, 37% of associate professors, and 21% of full professors in business schools (Morgan et al., 2021). The pandemic arguably widened this gender gap, but little systemic data exists to quantify it. Our study set out to answer two questions: (1) How much will the COVID-19 pandemic have impacted the gender gap in U.S. business school tenured and tenure-track faculty? and (2) How much will institutional policies designed to help faculty members during the pandemic have affected this gender gap? We used agent-based modeling coupled with archival data to develop a simulation of the tenure process in business schools in the U.S. and tested how institutional interventions would affect this gender gap. Our simulations demonstrated that the gender gap in U.S. business schools was on track to close but would need further interventions to reach equality (50% females). In the long-term picture, COVID-19 had a small impact on the gender gap, as did dependent care assistance and tenure extensions (unless only women received tenure extensions). Changing performance evaluation methods to better value teaching and service activities and increasing the proportion of female new hires would help close the gender gap faster.
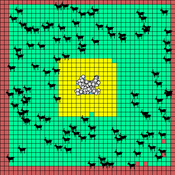
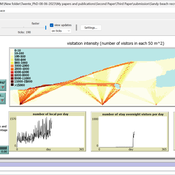
Sandy Beach Visitor Flow: An Agent-Based Model
Elham Bakhshianlamouki | Published Thursday, March 14, 2024The model is intended to simulate visitor spatial and temporal dynamics, encompassing their numbers, activities, and distribution along a coastline influenced by beach landscape design. Our primary focus is understanding how the spatial distribution of services and recreational facilities (e.g., beach width, entrance location, recreational facilities, parking availability) impacts visitation density. Our focus is not on tracking the precise visitation density but rather on estimating the areas most affected by visitor activity. This comprehension allows for assessing the diverse influences of beach layouts on spatial visitor density and, consequently, on the landscape’s biophysical characteristics (e.g., vegetation, fauna, and sediment features).
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Ramsey growth model with Brown and Green capital (ABRam-BG)
Sarah Wolf Aida Sarai Figueroa Alvarez | Published Monday, December 09, 2024The purpose of the ABRam-BG model is to study belief dynamics as a potential driver of green (growth) transitions and illustrate their dynamics in a closed, decentralized economy populated by utility maximizing agents with an environmental attitude. The model is built using the ABRam-T model (for model visit: https://doi.org/10.25937/ep45-k084) and introduces two types of capital – green (low carbon intensity) and brown (high carbon intensity) – with their respective technological progress levels. ABRam-BG simulates a green transition as an emergent phenomenon resulting from well-known opinion dynamics along the economic process.
Central-place forager mobility and cultural diversity
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, May 18, 2016This spatially explicit agent-based model addresses how effective foraging radius (r_e) affects the effective size–and thus the equilibrium cultural diversity–of a structured population composed of central-place foraging groups.
Displaying 10 of 119 results for "Ryan Long" clear search