About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 519 results for "Mark Orr" clear search
FlipFlop1-ProMEERB: A coupled social-ecological model with a promotional mechanism for emergence of environmentally responsible behavior
Liliana Perez Saeed Harati Roberto Molowny-Horas | Published Friday, December 17, 2021At the heart of a study of Social-Ecological Systems, this model is built by coupling together two independently developed models of social and ecological phenomena. The social component of the model is an abstract model of interactions of a governing agent and several user agents, where the governing agent aims to promote a particular behavior among the user agents. The ecological model is a spatial model of spread of the Mountain Pine Beetle in the forests of British Columbia, Canada. The coupled model allowed us to simulate various hypothetical management scenarios in a context of forest insect infestations. The social and ecological components of this model are developed in two different environments. In order to establish the connection between those components, this model is equipped with a ‘FlipFlop’ - a structure of storage directories and communication protocols which allows each of the models to process its inputs, send an output message to the other, and/or wait for an input message from the other, when necessary. To see the publications associated with the social and ecological components of this coupled model please see the References section.
Peer reviewed Personnel decisions in the hierarchy
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Friday, August 19, 2022This is a model of organizational behavior in the hierarchy in which personnel decisions are made.
The idea of the model is that the hierarchy, busy with operations, is described by such characteristics as structure (number and interrelation of positions) and material, filling these positions (persons with their individual performance). A particular hierarchy is under certain external pressure (performance level requirement) and is characterized by the internal state of the material (the distribution of the perceptions of others over the ensemble of persons).
The World of the model is a four-level hierarchical structure, consisting of shuff positions of the top manager (zero level of the hierarchy), first-level managers who are subordinate to the top manager, second-level managers (subordinate to the first-level managers) and positions of employees (the third level of the hierarchy). ) subordinated to the second-level managers. Such a hierarchy is a tree, i.e. each position, with the exception of the position of top manager, has a single boss.
Agents in the model are persons occupying the specified positions, the number of persons is set by the slider (HumansQty). Personas have some operational performance (harisma, an unfortunate attribute name left over from the first edition of the model)) and a sense of other personas’ own perceptions. Performance values are distributed over the ensemble of persons according to the normal law with some mean value and variance.
The value of perception by agents of each other is positive or negative (implemented in the model as numerical values equal to +1 and -1). The distribution of perceptions over an ensemble of persons is implemented as a random variable specified by the probability of negative perception, the value of which is set by the control elements of the model interface. The numerical value of the probability equal to 0 corresponds to the case in which all persons positively perceive each other (the numerical value of the random variable is equal to 1, which corresponds to the positive perception of the other person by the individual).
The hierarchy is occupied with operational activity, the degree of intensity of which is set by the external parameter Difficulty. The level of productivity of each manager OAIndex is equal to the level of productivity of the department he leads and is the ratio of the sum of productivity of employees subordinate to the head to the level of complexity of the work Difficulty. An increase in the numerical value of Difficulty leads to a decrease in the OAIndex for all subdivisions of the hierarchy. The managerial meaning of the OAIndex indicator is the percentage of completion of the load specified for the hierarchy as a whole, i.e. the ratio of the actual performance of the structural subdivisions of the hierarchy to the required performance, the level of which is specified by the value of the Difficulty parameter.
…
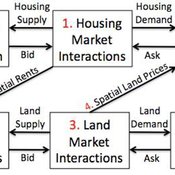
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
U-TRANS Modelling Urban Transition with Coupled Housing and Labour Markets
Bernardo Furtado Jiaqi Ge | Published Monday, July 31, 2023We develop an agent-based model (U-TRANS) to simulate the transition of an abstract city under an industrial revolution. By coupling the labour and housing markets, we propose a holistic framework that incorporates the key interacting factors and micro processes during the transition. Using U-TRANS, we look at five urban transition scenarios: collapse, weak recovery, transition, enhanced training and global recruit, and find the model is able to generate patterns observed in the real world. For example, We find that poor neighbourhoods benefit the most from growth in the new industry, whereas the rich neighbourhoods do better than the rest when the growth is slow or the situation deteriorates. We also find a (subtle) trade-off between growth and equality. The strategy to recruit a large number of skilled workers globally will lead to higher growth in GDP, population and human capital, but it will also entail higher inequality and market volatility, and potentially create a divide between the local and international workers. The holistic framework developed in this paper will help us better understand urban transition and detect early signals in the process. It can also be used as a test-bed for policy and growth strategies to help a city during a major economic and technological revolution.
An Agent-Based Model for Skilled Workers Migration
Hassan Bashiri | Published Thursday, September 21, 2023This documentation provides an overview and explanation of the NetLogo simulation code for modeling skilled workers’ migration in Iran. The simulation aims to explore the dynamics of skilled workers’ migration and their transition through various states, including training, employment, and immigration.
The flow of elite and talent migration, or “brain drain,” is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for developing countries. The decision to migrate is made due to various factors including economic opportunities, political stability, social factors and personal circumstances.
Measuring individual interests in the field of immigration is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. The agent-based model is a useful tool for understanding the complex factors that are involved in talent migration. By considering the various social, economic, and personal factors that influence migration decisions, policymakers can provide more effective strategies to retain skilled and talented labor and promote sustainable growth in developing countries. One of the main challenges in studying the flow of elite migration is the complexity of the decision-making process and a set of factors that lead to migration decisions. Agent-based modeling is a useful tool for understanding how individual decisions can lead to large-scale migration patterns.
Agent-based model of power dynamics in agri-food systems
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, October 27, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, June 12, 2025This is a stylised agent-based model designed to explore the conditions that lead to lock-ins and transitions in agri-food systems.
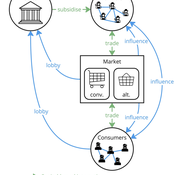
The model represents interactions between four different types of agents: farmers, consumers, markets, and the state. Farmers and consumers are heterogeneous, and at each time step decide whether to trade with one of two market agents: the conventional or alternative. The state agent provides subsidies to the farmers at each time step.
The key emergent outcome is the fraction of trade in each time step that flows through the alternative market agent. This arises from the distributed decisions of farmer and consumer agents. A “sustainability transition” is defined as a shift in the dominant practices (and associated balance of power) towards the alternative paradigm.
…
Hyperconnectivity, and Fact-Checking- Modeling Witnessing as a Traditional Coast Salish Mechanism
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Thursday, May 01, 2025An unintended consequence of low cost maritime travel may be hyperconnectedness, creating social situations where information can be readily passed before it is verified- an issue not limited to modern digitally connected societies. In traditional Coast Salish societies, the peoples of what is now Western Washington and Southwestern British Columbia, oral traditions were vertified through a process called witnessing. Witnesses would be trained to recount and verify oral history and traditional teachings at high fidelity. Here, a simple model based on dual inheritance approaches to genes and culture, is used to compare this specific form of verifying socially important information compared to modern mass communication. The model suggests that witnessing is a high fidelity form of transmitting knowledge with a low error rate, more in line with modern apprenticeships than mass communication. Social mechanisms such as witnessing provide solutions to issues faced in contemporary discourse where the validity of information and even fact checking mechanisms may be biased or counterfactual. This effort also demonstrates the utillity of using modeling approaches to highlight how specific, historically contingent institutions such as witnesses can be drawn upon to model potential solutions to contemporary issues solved in the past in traditional Coast Salish practice.
Risks and Hedonics in Empirical Agent-based land market (RHEA) model
Tatiana Filatova Koen de Koning | Published Monday, April 01, 2019RHEA aims to provide a methodological platform to simulate the aggregated impact of households’ residential location choice and dynamic risk perceptions in response to flooding on urban land markets. It integrates adaptive behaviour into the spatial landscape using behavioural theories and empirical data sources. The platform can be used to assess: how changes in households’ preferences or risk perceptions capitalize in property values, how price dynamics in the housing market affect spatial demographics in hazard-prone urban areas, how structural non-marginal shifts in land markets emerge from the bottom up, and how economic land use systems react to climate change. RHEA allows direct modelling of interactions of many heterogeneous agents in a land market over a heterogeneous spatial landscape. As other ABMs of markets it helps to understand how aggregated patterns and economic indices result from many individual interactions of economic agents.
The model could be used by scientists to explore the impact of climate change and increased flood risk on urban resilience, and the effect of various behavioural assumptions on the choices that people make in response to flood risk. It can be used by policy-makers to explore the aggregated impact of climate adaptation policies aimed at minimizing flood damages and the social costs of flood risk.
An agent-based model of building occupant behavior during load shedding
Handi Chandra Putra | Published Thursday, May 21, 2020Load shedding enjoys increasing popularity as a way to reduce power consumption in buildings during hours of peak demand on the electricity grid. This practice has well known cost saving and reliability benefits for the grid, and the contracts utilities sign with their “interruptible” customers often pass on substantial electricity cost savings to participants. Less well-studied are the impacts of load shedding on building occupants, hence this study investigates those impacts on occupant comfort and adaptive behaviors. It documents experience in two office buildings located near Philadelphia (USA) that vary in terms of controllability and the set of adaptive actions available to occupants. An agent-based model (ABM) framework generalizes the case-study insights in a “what-if” format to support operational decision making by building managers and tenants. The framework, implemented in EnergyPlus and NetLogo, simulates occupants that have heterogeneous
thermal and lighting preferences. The simulated occupants pursue local adaptive actions such as adjusting clothing or using portable fans when central building controls are not responsive, and experience organizational constraints, including a corporate dress code and miscommunication with building managers. The model predicts occupant decisions to act fairly well but has limited ability to predict which specific adaptive actions occupants will select.
Peer reviewed Organizational behavior in the hierarchy model
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, July 31, 2019In a two-level hierarchical structure (consisting of the positions of managers and operators), persons holding these positions have a certain performance and the value of their own (personal perception in this, simplified, version of the model) perception of each other. The value of the perception of each other by agents is defined as a random variable that has a normal distribution (distribution parameters are set by the control elements of the interface).
In the world of the model, which is the space of perceptions, agents implement two strategies: rapprochement with agents that perceive positively and distance from agents that perceive negatively (both can be implemented, one of these strategies, or neither, the other strategy, which makes the agent stationary). Strategies are implemented in relation to those agents that are in the radius of perception (PerRadius).
The manager (Head) forms a team of agents. The performance of the group (the sum of the individual productivities of subordinates, weighted by the distance from the leader) varies depending on the position of the agents in space and the values of their individual productivities. Individual productivities, in the current version of the model, are set as a random variable distributed evenly on a numerical segment from 0 to 100. The manager forms the team 1) from agents that are in (organizational) radius (Op_Radius), 2) among agents that the manager perceives positively and / or negatively (both can be implemented, one of the specified rules, or neither, which means the refusal of the command formation).
Agents can (with a certain probability, given by the variable PrbltyOfDecisn%), in case of a negative perception of the manager, leave his group permanently.
It is possible in the model to change on the fly radii values, update the perception value across the entire population and the perception of an individual agent by its neighbors within the perception radius, and the probability values for a subordinate to make a decision about leaving the group.
You can also change the set of strategies for moving agents and strategies for recruiting a team manager. It is possible to add a randomness factor to the movement of agents (Stoch_Motion_Speed, the default is set to 0, that is, there are no random movements).
…
Displaying 10 of 519 results for "Mark Orr" clear search