About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 477 results social clear search
Model of Context Switching with Segregation
Davide Nunes | Published Thursday, August 02, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In the context switching model, a society of agents embedded in multiple social relations, engages in a simple abstract game: the consensus game. Each agent has to choose towards one of two possible choices which are basically arbitrary. The objective of the game is to reach a global consensus, but the particular choice that gets collectively selected is irrelevant.
Irrigation game
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, July 23, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Irrigation game calibrated on experimental data
MayaSim: An agent-based model of the ancient Maya social-ecological system
Scott Heckbert | Published Wednesday, July 11, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, July 02, 2013MayaSim is an agent-based, cellular automata and network model of the ancient Maya. Biophysical and anthropogenic processes interact to grow a complex social ecological system.
A simple Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of the Commons (MASTOC-s)
Julia Schindler | Published Friday, June 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a simple model replicating Hardin’s Tragedy of the Commons using reactive agents that have psychological behavioral and social preferences.
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
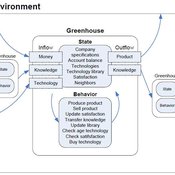
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
An Agent-Based Model of Internet Diffusion Under General and Specific Network Externalities
Filiz Garip | Published Friday, April 27, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Using nodes from the 2002 General Social Survey sample, the code establishes a network of ties with a given homophily bias, and simulates Internet adoption rates in that network under three conditions: (i) no network externalities, (ii) general network externalities, where an individual’s reservation price is a function of the overall adoption rate in the network, (iii) specific network externalities, where reservation price is a function of the adoption rate in individual’s personal […]
Social Nets Emergence Model
Di Wang | Published Wednesday, March 21, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates the interactions and dynamic trust changes between people which results in social group emergence and evolution.
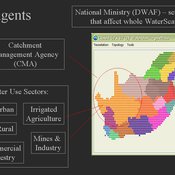
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Displaying 10 of 477 results social clear search