About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search
Cellular automata model of social networks
Rubens de Almeida Zimbres | Published Tuesday, August 02, 2022This project was developed during the Santa Fe course Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling 2022. The origin is a Cellular Automata (CA) model to simulate human interactions that happen in the real world, from Rubens and Oliveira (2009). These authors used a market research with real people in two different times: one at time zero and the second at time zero plus 4 months (longitudinal market research). They developed an agent-based model whose initial condition was inherited from the results of the first market research response values and evolve it to simulate human interactions with Agent-Based Modeling that led to the values of the second market research, without explicitly imposing rules. Then, compared results of the model with the second market research. The model reached 73.80% accuracy.
In the same way, this project is an Exploratory ABM project that models individuals in a closed society whose behavior depends upon the result of interaction with two neighbors within a radius of interaction, one on the relative “right” and other one on the relative “left”. According to the states (colors) of neighbors, a given cellular automata rule is applied, according to the value set in Chooser. Five states were used here and are defined as levels of quality perception, where red (states 0 and 1) means unhappy, state 3 is neutral and green (states 3 and 4) means happy.
There is also a message passing algorithm in the social network, to analyze the flow and spread of information among nodes. Both the cellular automaton and the message passing algorithms were developed using the Python extension. The model also uses extensions csv and arduino.
Peer reviewed An agent-based model for brain drain
Furkan Gürsoy Bertan Badur | Published Wednesday, March 03, 2021 | Last modified Friday, March 12, 2021An agent-based model for the emigration of highly-skilled labour.
We hypothesise that there are two main factors that impact the decision and ability to move abroad: desire to maximise individual utility and network effects. Accordingly, several factors play role in brain drain such as the overall economic and social differences between the home and host countries, people’s ability and capacity to obtain good jobs and start a life abroad, the barriers of moving abroad, and people’s social network who are already working abroad.
The uFUNK Model
Davide Secchi | Published Monday, August 31, 2020The agent-based simulation is set to work on information that is either (a) functional, (b) pseudo-functional, (c) dysfunctional, or (d) irrelevant. The idea is that a judgment on whether information falls into one of the four categories is based on the agent and its network. In other words, it is the agents who interprets a particular information as being (a), (b), (c), or (d). It is a decision based on an exchange with co-workers. This makes the judgment a socially-grounded cognitive exercise. The uFUNK 1.0.2 Model is set on an organization where agent-employee work on agent-tasks.
Enhancing recycling of construction materials; an agent based model with empirically based decision parameters
Igor Nikolic Claudia Binder Christof Knoeri Hans-Joerg Althaus | Published Sunday, October 21, 2012 | Last modified Monday, June 09, 2014This model allows for analyzing the most efficient levers for enhancing the use of recycled construction materials, and the role of empirically based decision parameters.
Knowledge Sharing in a Hospital
bpint Emily Molfino Joshua Goldstein Kathryn Schaefer Ziemer Mark Orr Bryan Lewis Jose Jimenez | Published Friday, January 27, 2023Organizations are complex systems comprised of many dynamic and evolving interaction patterns among individuals and groups. Understanding these interactions and how patterns, such as informal structures and knowledge sharing behavior, emerge are crucial to creating effective and efficient organizations. To explore such organizational dynamics, the agent-based model integrates a cognitive model, dynamic social networks, and a physical environment.
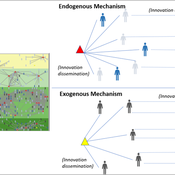
Peer reviewed Modelling Agricultural Innovations as a Social-Ecological Phenomenon
Maja Schlüter Udita Sanga | Published Thursday, November 17, 2022The goal of the AG-Innovation agent-based model is to explore and compare the effects of two alternative mechanisms of innovation development and diffusion (exogenous, linear and endogenous, non-linear) on emergent properties of food and income distribution and adoption rates of different innovations. The model also assesses the range of conditions under which these two alternative mechanisms would be effective in improving food security and income inequality outcomes. Our modelling questions were: i) How do cross-scalar social-ecological interactions within agricultural innovation systems affect system outcomes of food security and income inequality? ii) Do foreign aid-driven exogenous innovation perpetuate income inequality and food insecurity and if so, under which conditions? iii) Do community-driven endogenous innovations improve food security and income inequality and if so, under which conditions? The Ag-Innovation model is intended to serve as a thinking tool for for the development and testing of hypotheses, generating an understanding of the behavior of agricultural innovation systems, and identifying conditions under which alternated innovation mechanisms would improve food security and income inequality outcomes.
An agent-based model to simulate field-specific nitrogen fertilizer applications in grasslands
Maria Haensel Thomas Schmitt Andrea Kaim Sylvia Helena Annuth Thomas Koellner | Published Sunday, February 09, 2025Grasslands have a large share of the world’s land cover and their sustainable management is important for the protection and provisioning of grassland ecosystem services. The question of how to manage grassland sustainably is becoming increasingly important, especially in view of climate change, which on the one hand extends the vegetation period (and thus potentially allows use intensification) and on the other hand causes yield losses due to droughts. Fertilization plays an important role in grassland management and decisions are usually made at farm level. Data on fertilizer application rates are crucial for an accurate assessment of the effects of grassland management on ecosystem services. However, these are generally not available on farm/field scale. To close this gap, we present an agent-based model for Fertilization In Grasslands (FertIG). Based on animal, land-use, and cutting data, the model estimates grassland yields and calculates field-specific amounts of applied organic and mineral nitrogen on grassland (and partly cropland). Furthermore, the model considers different legal requirements (including fertilization ordinances) and nutrient trade among farms. FertIG was applied to a grassland-dominated region in Bavaria, Germany comparing the effects of changes in the fertilization ordinance as well as nutrient trade. The results show that the consideration of nutrient trade improves organic fertilizer distribution and leads to slightly lower Nmin applications. On a regional scale, recent legal changes (fertilization ordinance) had limited impacts. Limiting the maximum applicable amount of Norg to 170 kg N/ha fertilized area instead of farm area as of 2020 hardly changed fertilizer application rates. No longer considering application losses in the calculation of fertilizer requirements had the strongest effects, leading to lower supplementary Nmin applications. The model can be applied to other regions in Germany and, with respective adjustments, in Europe. Generally, it allows comparing the effects of policy changes on fertilization management at regional, farm and field scale.
Multi Asset Variable Network Stock Market Model
Matthew Oldham | Published Monday, September 12, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, October 10, 2017An artifcal stock market model that allows users to vary the number of risky assets as well as the network topology that investors forms in an attempt to understand the dynamics of the market.
3D Urban Traffic Simulator (ABM) in Unity
Daniel Birks Sedar Olmez Obi Thompson Sargoni Alison Heppenstall Annabel Whipp Ed Manley | Published Friday, January 22, 2021 | Last modified Monday, March 22, 2021The Urban Traffic Simulator is an agent-based model developed in the Unity platform. The model allows the user to simulate several autonomous vehicles (AVs) and tune granular parameters such as vehicle downforce, adherence to speed limits, top speed in mph and mass. The model allows researchers to tune these parameters, run the simulator for a given period and export data from the model for analysis (an example is provided in Jupyter Notebook).
The data the model is currently able to output are the following:
…
A simple Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of the Commons (MASTOC-s)
Julia Schindler | Published Friday, June 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a simple model replicating Hardin’s Tragedy of the Commons using reactive agents that have psychological behavioral and social preferences.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search