About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 439 results for "Therese Lindahl" clear search
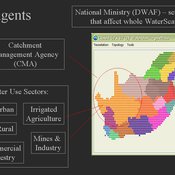
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Human mate choice is a complex system
Paul Smaldino Jeffrey C Schank | Published Friday, February 08, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A general model of human mate choice in which agents are localized in space, interact with close neighbors, and tend to range either near or far. At the individual level, our model uses two oft-used but incompletely understood decision rules: one based on preferences for similar partners, the other for maximally attractive partners.
Individual bias and organizational objectivity
Bo Xu | Published Monday, April 15, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model introduces individual bias to the model of exploration and exploitation, simulates knowledge diffusion within organizations, aiming to investigate the effect of individual bias and other related factors on organizational objectivity.
Agent-based model of risk behavior in adolescence
N Schuhmacher P Van Geert L Ballato | Published Monday, June 24, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The computer model simulates the development of a social network (i.e. formation of friendships and cliques), the (dyadic) interactions between pupils and the development of similarities and differences in their behavioral profiles.
ForagerNet3_Demography: A Non-Spatial Model of Hunter-Gatherer Demography
Andrew White | Published Thursday, October 17, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 17, 2013ForagerNet3_Demography is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. Key methods represent birth, death, and marriage. The dependency ratio is an imporant variable in many economic decisions embedded in the methods.
Mobility USA (MUSA)
Giangiacomo Bravo Davide Natalini | Published Sunday, December 08, 2013 | Last modified Monday, December 30, 2013MUSA is an ABM that simulates the commuting sector in USA. A multilevel validation was implemented. Social network with a social-circle structure included. Two types of policies have been tested: market-based and preference-change.
ForagerNet3_Demography_V2
Andrew White | Published Thursday, February 13, 2014ForagerNet3_Demography_V2 is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. This version (developed from FN3D_V1) contains code for calculating the ratio of old to young adults (the “OY ratio”) in the living and dead populations.
An Agent-Based School Choice Matching Model
Connie Wang Weikai Chen Shu-Heng Chen | Published Sunday, February 01, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, March 06, 2019This model is to simulate and compare the admission effects of 3 school matching mechanisms, serial dictatorship, Boston mechanism, and Chinese Parallel, under different settings of information released.
Homophily-driven Network Evolution and Diffusion
Gönenç Yücel Mustafa Yavaş | Published Thursday, January 08, 2015The model is an experimental ground to study the impact of network structure on diffusion. It allows to construct a social network that already has some measurable level of homophily, and simulate a diffusion process over this social network.
PA/C model with affinity
N. Leticia Abrica-Jacinto Evguenii Kurmyshev Héctor Juárez | Published Thursday, October 27, 2016We expose RA agent-based model of the opinion and tolerance dynamics in artificial societies. The formal mathematical model is based on the ideas of Social Influence, Social Judgment, and Social Identity theories.
Displaying 10 of 439 results for "Therese Lindahl" clear search