About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1116 results for "A Flache" clear search
Nice Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Friday, February 05, 2016 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2017The Nice Musical Chairs (NMC) model represent the competition for space between groups of stakeholders of farming and herding activities in the arid Afro-Eurasia.
Socio-hydrologicalModel_version_SESMO
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Paola Gomez Luis Bojorquez Fidel Serrano-Candela Hallie Eakin Yosune Miquelajauregui Rodrigo Garcia-Herrera | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We present here MEGADAPT_SESMO model. A hybrid, dynamic, spatially explicit, integrated model to simulate the vulnerability of urban coupled socio-ecological systems – in our case, the vulnerability of Mexico City to socio-hydrological risk.
Formal Organization Hierarchy and Informal Networks - "The Company Behind the Org Chart"
Tom Briggs | Published Sunday, April 18, 2021A generalized organizational agent- based model (ABM) containing both formal organizational hierarchy and informal social networks simulates organizational processes that occur over both formal network ties and informal networks.
Peer reviewed E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
TERRoir level Organic matter Interactions and Recycling model
Myriam Grillot | Published Wednesday, April 19, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, June 17, 2020The TERROIR agent-based model was built for the multi-level analysis of biomass and nutrient flows within agro-sylvo-pastoral villages in West Africa. It explicitly takes into account both human organization and spatial extension of such flows.
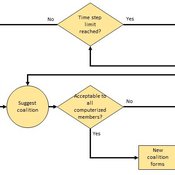
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
Peer reviewed HUMLAND FIRE-IN-THE-HOLE agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina | Published Monday, October 20, 2025HUMLAND Fire-in-the-Hole is a conceptual agent-based model (ABM) designed to explore the ecological and behavioral consequences of fire-driven hunting strategies employed by hunter-gatherers, specifically Neanderthals, during the Last Interglacial period around the Neumark-Nord (Germany) archaeological site.
This model builds on and specializes the HUMLAND 1.0.0 model (Nikulina et al. 2024), integrating anthropogenic fires, elephant group behavior, and landscape response to simulate interactions between humans, megafauna, and vegetation over time.
Political Participation
Didier Ruedin | Published Saturday, April 12, 2014 | Last modified Sunday, September 28, 2025Implementation of Milbrath’s (1965) model of political participation. Individual participation is determined by stimuli from the political environment, interpersonal interaction, as well as individual characteristics.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
The emergence of tag-mediated altruism in structured societies
Shade Shutters David Hales | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, March 02, 2023This abstract model explores the emergence of altruistic behavior in networked societies. The model allows users to experiment with a number of population-level parameters to better understand what conditions contribute to the emergence of altruism.
Displaying 10 of 1116 results for "A Flache" clear search