About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 477 results social clear search
3spire: an agent-based model for exploring aspiration adaptation theory and its implications on smallholder farmers in Ethiopia
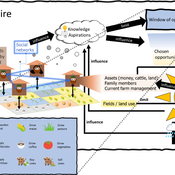
ateeuw Yue Dou Markus A Meyer Andrew Nelson | Published Sunday, February 16, 20253spire is an ABM where farming households make management decisions aimed at satisficing along the aspirational dimensions: food self-sufficiency, income, and leisure. Households decision outcomes depend on their social networks, knowledge, assets, household needs, past management, and climate/market trends
An Agent-Based Model of Indirect Minority Influence on Social Change
Jiin Jung | Published Wednesday, February 05, 2025This model demonstrates how different psychological mechanisms and network structures generate various patterns of cultural dynamics including cultural diversity, polarization, and majority dominance, as explored by Jung, Bramson, Crano, Page, and Miller (2021). It focuses particularly on the psychological mechanisms of indirect minority influence, a concept introduced by Serge Moscovici (1976, 1980)’s genetic model of social influence, and validates how such influence can lead to social change.
Autonomy or control? An agent-based study of self-organising versus centralised task allocation
Shaoni Wang | Published Wednesday, January 29, 2025The aim of our model is to investigate the team dynamics through two types of task allocation strategies, with a focus on the dynamic interplay between individual needs and group performance. To achieve this goal, we have formulated an agent-based model (ABM) to formalize Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) and explore the social dynamics that govern the relationship between individual and group levels of team performance.
ABM Code: Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries
Diego Leal | Published Thursday, January 23, 2025The code and data in this repository are associated with the article titled: “Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries.” The NetLogo code (version 6.4.0) is designed to be a standalone piece of code although it uses the ‘nw’ and ‘matrix’ extensions that come integrated with NetLogo 6.4.0. The code was ran on a Windows 10 x 64 machine.
MeReDiem : Fallow Land Simulations to examine the conditions of sustainable village livelihood
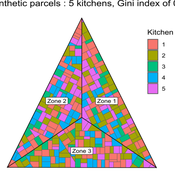
Etienne DELAY Paul Chapron Mathieu | Published Monday, January 20, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2025The MeReDiem model aims to simulate the effect of socio-agricultural practices of farmers and pastors on the food sustainability and soil fertility of a serrer village, in Senegal. The model is a central part of a companion modeling and exploration approach, described in a paper, currently under review)
The village population is composed of families (kitchens). Kitchens cultivate their land parcels to feed their members, aiming for food security at the family level. On a global level , the village tries to preserve the community fallow land as long as possible.
Kitchens sizes vary depending on the kitchens food production, births and migration when food is insufficient.
…
Soy2Grow-ABM-V1
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Monday, January 20, 2025The Soy2Grow ABM aims to simulate the adoption of soybean production in Flanders, Belgium. The model primarily considers two types of agents as farmers: 1) arable and 2) dairy farmers. Each farmer, based on its type, assesses the feasibility of adopting soybean cultivation. The feasibility assessment depends on many interrelated factors, including price, production costs, yield, disease, drought (i.e., environmental stress), social pressure, group formations, learning and skills, risk-taking, subsidies, target profit margins, tolerance to bad experiences, etc. Moreover, after adopting soybean production, agents will reassess their performance. If their performance is unsatisfactory, an agent may opt out of soy production. Therefore, one of the main outcomes to look for in the model is the number of adopters over time.
The main agents are farmers. Generally, factors influencing farmers’ decision-making are divided into seven main areas: 1) external environmental factors, 2) cooperation and learning (with slight differences depending on whether they are arable or dairy farmers), 3) crop-specific factors, 4) economics, 5) support frameworks, 6) behavioral factors, and 7) the role of mobile toasters (applicable only to dairy farmers).
Moreover, factors not only influence decision-making but also interact with each other. Specifically, external environmental factors (i.e., stress) will result in lower yield and quality (protein content). The reducing effect, identified during participatory workshops, can reach 50 %. Skills can grow and improve yield; however, their growth has a limit and follows different learning curves depending on how individualistic a farmer is. During participatory workshops, it was identified that, contrary to cooperative farmers, individualistic farmers may learn faster and reach their limits more quickly. Furthermore, subsidies directly affect revenues and profit margins; however, their impact may disappear when they are removed. In the case of dairy farmers, mobile toasters play an important role, adding toasting and processing costs to those producing soy for their animal feed consumption.
Last but not least, behavioral factors directly influence the final adoption decision. For example, high risk-taking farmers may adopt faster, whereas more conservative farmers may wait for their neighbors to adopt first. Farmers may evaluate their success based on their own targets and may also consider other crops rather than soy.
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
Gini Palma microsimulation
Edgar Oliveira | Published Wednesday, December 11, 2024The model is a microsimulation, where the agents don’t Interact with each other. It simulates income distribution, unemployment dynamics, education, and Family grant in Brazil, focusing on the impact on social inequality. It tracks the indicators Gini index, Lorenz curve, and Palma ratio. The objective is to explore how these factors influence wealth distribution and social inequality over time.
This work was developed in partnership with the Graduate Program in Computational Modeling, in the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande - FURG, in Brazil.
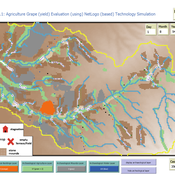
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
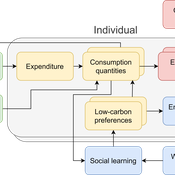
The cultural multiplier of climate policy
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Thursday, October 31, 2024For deep decarbonisation, the design of climate policy needs to account for consumption choices being influenced not only by pricing but also by social learning. This involves changes that pertain to the whole spectrum of consumption, possibly involving shifts in lifestyles. In this regard, it is crucial to consider not just short-term social learning processes but also slower, longer-term, cultural change. Against this background, we analyse the interaction between climate policy and cultural change, focusing on carbon taxation. We extend the notion of “social multiplier” of environmental policy derived in an earlier study to the context of multiple consumer needs while allowing for behavioural spillovers between these, giving rise to a “cultural multiplier”. We develop a model to assess how this cultural multiplier contributes to the effectiveness of carbon taxation. Our results show that the cultural multiplier stimulates greater low-carbon consumption compared to fixed preferences. The model results are of particular relevance for policy acceptance due to the cultural multiplier being most effective at low-carbon tax values, relative to a counter-case of short-term social interactions. Notably, at high carbon tax levels, the distinction between social and cultural multiplier effects diminishes, as the strong price signal drives even resistant individuals toward low-carbon consumption. By varying socio-economic conditions, such as substitutability between low- and high-carbon goods, social network structure, proximity of like-minded individuals and the richness of consumption lifestyles, the model provides insight into how cultural change can be leveraged to induce maximum effectiveness of climate policy.
Displaying 10 of 477 results social clear search