About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 935 results for "Jan Van Bavel" clear search
A spatial model of resource-consumer dynamics
Arend Ligtenberg Guus Ten Broeke George Ak Van Voorn Jaap Molenaar | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, September 17, 2020The model simulates agents in a spatial environment competing for a common resource that grows on patches. The resource is converted to energy, which is needed for performing actions and for surviving.
Mission San Diego Model
Carolyn Orbann | Published Monday, April 15, 2019The Mission San Diego model is an epidemiological model designed to test hypotheses related to the spread of the 1805-1806 measles epidemic among indigenous residents of Mission San Diego during the early mission period in Alta California. The model community is based on the population of the Mission San Diego community, as listed in the parish documents (baptismal, marriage, and death records). Model agents are placed on a map-like grid that consists of houses, the mission church, a women’s dormitory (monjeria) adjacent to the church, a communal kitchen, priest’s quarters, and agricultural fields. They engage in daily activities that reflect known ethnographic patterns of behavior at the mission. A pathogen is introduced into the community and then it spreads throughout the population as a consequence of individual agent movements and interactions.
THE STATUS ARENA
Gert Jan Hofstede Jillian Student Mark R Kramer | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 09, 2018Status-power dynamics on a playground, resulting in a status landscape with a gender status gap. Causal: individual (beauty, kindness, power), binary (rough-and-tumble; has-been-nice) or prior popularity (status). Cultural: acceptability of fighting.
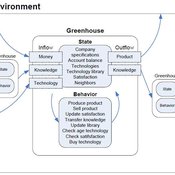
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Industrial Cooperation and the Hydrogen Transition
Amineh Ghorbani Renske van 't Veer Emre Ates Zofia Lukszo | Published Tuesday, September 23, 2025An Agent Based Model that explores the deployment of hydrogen among a regional industrial cluster in the Netherlands, consisting of 15 companies. The companies seek to decarbonize by replacing their natural gas by hydrogen.
The model integrates technical characteristics as well as company motivations to transition to hydrogen. The baseline model only considers individual investments where company can locally produce hydrogen. If they reach the backbone threshold, companies can also consider buying hydrogen through a connection to the national hydrogen network. The second scenario considers that companies can participate in a joint investment to get an electrolyzer to locally produce the hydrogen.
Two experiments look at the impact of the sectoral configuration and at the impact of subsidy conditions on the region’s hydrogen transition
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
Peer reviewed Garbage can model NetLogo implementation
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Sunday, February 14, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019It is NetLogo reconstruction of the original FORTRAN code of the classical M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen “garbage can model” (GCM or CMO) of collective decision-making.
Gender Disparity in COVID-19’s Impact on Academic Careers: An Agent-Based Model
S.R. Aurora (a.k.a. Mai P. Trinh) Chantal van Esch | Published Tuesday, September 26, 2023Prior to COVID-19, female academics accounted for 45% of assistant professors, 37% of associate professors, and 21% of full professors in business schools (Morgan et al., 2021). The pandemic arguably widened this gender gap, but little systemic data exists to quantify it. Our study set out to answer two questions: (1) How much will the COVID-19 pandemic have impacted the gender gap in U.S. business school tenured and tenure-track faculty? and (2) How much will institutional policies designed to help faculty members during the pandemic have affected this gender gap? We used agent-based modeling coupled with archival data to develop a simulation of the tenure process in business schools in the U.S. and tested how institutional interventions would affect this gender gap. Our simulations demonstrated that the gender gap in U.S. business schools was on track to close but would need further interventions to reach equality (50% females). In the long-term picture, COVID-19 had a small impact on the gender gap, as did dependent care assistance and tenure extensions (unless only women received tenure extensions). Changing performance evaluation methods to better value teaching and service activities and increasing the proportion of female new hires would help close the gender gap faster.
Peer reviewed Monogamous Reproduction in Small Populations and the Enforcement of the Incest Taboo
Ian Stuart | Published Wednesday, January 18, 2023This program was developed to simulate monogamous reproduction in small populations (and the enforcement of the incest taboo).
Every tick is a year. Adults can look for a mate and enter a relationship. Adult females in a Relationship (under the age of 52) have a chance to become pregnant. Everyone becomes not alive at 77 (at which point people are instead displayed as flowers).
User can select a starting-population. The starting population will be adults between the ages of 18 and 42.
…
Peer reviewed A Macroeconomic Model of a Closed Economy
Ian Stuart | Published Saturday, May 08, 2021 | Last modified Wednesday, June 23, 2021This model/program presents a “three industry model” that may be particularly useful for macroeconomic simulations. The main purpose of this program is to demonstrate a mechanism in which the relative share of labor shifts between industries.
Care has been taken so that it is written in a self-documenting way so that it may be useful to anyone that might build from it or use it as an example.
This model is not intended to match a specific economy (and is not calibrated to do so) but its particular minimalist implementation may be useful for future research/development.
…
Displaying 10 of 935 results for "Jan Van Bavel" clear search