About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 158 results for "Daniele Vernon-Bido" clear search
A Model of Iterated Ultimatum game
Andrea Scalco | Published Tuesday, February 24, 2015 | Last modified Monday, March 09, 2015The simulation generates two kinds of agents, whose proposals are generated accordingly to their selfish or selfless behaviour. Then, agents compete in order to increase their portfolio playing the ultimatum game with a random-stranger matching.
CONSERVAT
Pieter Van Oel | Published Monday, April 13, 2015The CONSERVAT model evaluates the effect of social influence among farmers in the Lake Naivasha basin (Kenya) on the spatiotemporal diffusion pattern of soil conservation effort levels and the resulting reduction in lake sedimentation.
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
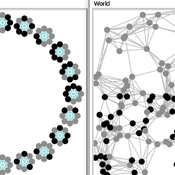
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
Lansing-Kremer model of the Balinese irrigation system
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, June 16, 2008 | Last modified Tuesday, December 16, 2014This is a NetLogo replication of the hill-climbing version of the Lansing-Kremer model of Balinese irrigation.
GODS: Gossip-Oriented Dilemma Simulator
Jan Majewski | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2024 | Last modified Monday, September 29, 2025Model of influence of access to social information spread via social network on decisions in a two-person game.
Endogenous dynamics of firms made up by networked agents: an exploratory analysis
Bernardo Alves Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Wednesday, March 23, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, October 05, 2016This is an adaptation and extension of Robert Axtell’s model (2013) of endogenous firms, in Python 3.4
Neminem laedere: Socially damaging behaviours and how to contain them
Nicola Lettieri | Published Wednesday, June 23, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013First version of the model “Neminem laedere. Socially damaging behaviours and how to contain them” by Domenico Parisi and Nicola Lettieri
A simple Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of the Commons (MASTOC-s)
Julia Schindler | Published Friday, June 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a simple model replicating Hardin’s Tragedy of the Commons using reactive agents that have psychological behavioral and social preferences.
Selene ABM Suite
ihctdy-f | Published Sunday, January 11, 2026Project Selene ABM Suite
Agent-Based Scenario Exploration for Consortium Cooperation Dynamics
Version: 2.1 (Revised)
Date: January 2026
Status: Exploratory Analysis Tool
Best Practices for Civic Collaboration
Wei Zhong | Published Saturday, December 20, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a modified version (Netlogo 4.0.3) of the model in support of Erik Johnstons dissertation, programmed in Netlogo 3.1.4 (May 15th, 2007).
Displaying 10 of 158 results for "Daniele Vernon-Bido" clear search