About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1116 results for "A Flache" clear search
Correlated random walk (Javascript)
Viktoriia Radchuk Uta Berger Thibault Fronville | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
In this script the turning angles (following the Von Mises distribution) are generated based on the the instructions from N. I. Fisher 2011.
This model is implemented in Javascript and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
3D Urban Traffic Simulator (ABM) in Unity
Daniel Birks Sedar Olmez Obi Thompson Sargoni Alison Heppenstall Annabel Whipp Ed Manley | Published Friday, January 22, 2021 | Last modified Monday, March 22, 2021The Urban Traffic Simulator is an agent-based model developed in the Unity platform. The model allows the user to simulate several autonomous vehicles (AVs) and tune granular parameters such as vehicle downforce, adherence to speed limits, top speed in mph and mass. The model allows researchers to tune these parameters, run the simulator for a given period and export data from the model for analysis (an example is provided in Jupyter Notebook).
The data the model is currently able to output are the following:
…
ReMoTe-S. Residential Mobility of Tenants in Switzerland: an agent-based model
Claudia Binder Anna Pagani Francesco Ballestrazzi Emanuele Massaro | Published Friday, April 01, 2022ReMoTe-S is an agent-based model of the residential mobility of Swiss tenants. Its goal is to foster a holistic understanding of the reciprocal influence between households and dwellings and thereby inform a sustainable management of the housing stock. The model is based on assumptions derived from empirical research conducted with three housing providers in Switzerland and can be used mainly for two purposes: (i) the exploration of what if scenarios that target a reduction of the housing footprint while accounting for households’ preferences and needs; (ii) knowledge production in the field of residential mobility and more specifically on the role of housing functions as orchestrators of the relocation process.
Peer reviewed HUMLAND2: HUMan impact on LANDscapes agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina Anhelina Zapolska Maria Antonia Serge Marco Davoli Dave van Wees Katharine MacDonald Elena A. Pearce | Published Friday, August 30, 2024The HUMan Impact on LANDscapes (HUMLAND) 2.0.0 is an enhanced version of HUMLAND 1.0.0, developed to track and quantify the intensity of various impacts on landscapes at a continental scale. The model is designed to identify the most influential factors in the transformation of interglacial vegetation, with a particular focus on the burning practices of hunter-gatherers. HUMLAND 2.0.0 incorporates a wide range of spatial datasets as both inputs and targets (expected modelling results) for simulations across Last Interglacial (~130,000–116,000 BP) and Early Holocene (~11,700–8,000 BP).
Peer reviewed Personnel decisions in the hierarchy
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Friday, August 19, 2022This is a model of organizational behavior in the hierarchy in which personnel decisions are made.
The idea of the model is that the hierarchy, busy with operations, is described by such characteristics as structure (number and interrelation of positions) and material, filling these positions (persons with their individual performance). A particular hierarchy is under certain external pressure (performance level requirement) and is characterized by the internal state of the material (the distribution of the perceptions of others over the ensemble of persons).
The World of the model is a four-level hierarchical structure, consisting of shuff positions of the top manager (zero level of the hierarchy), first-level managers who are subordinate to the top manager, second-level managers (subordinate to the first-level managers) and positions of employees (the third level of the hierarchy). ) subordinated to the second-level managers. Such a hierarchy is a tree, i.e. each position, with the exception of the position of top manager, has a single boss.
Agents in the model are persons occupying the specified positions, the number of persons is set by the slider (HumansQty). Personas have some operational performance (harisma, an unfortunate attribute name left over from the first edition of the model)) and a sense of other personas’ own perceptions. Performance values are distributed over the ensemble of persons according to the normal law with some mean value and variance.
The value of perception by agents of each other is positive or negative (implemented in the model as numerical values equal to +1 and -1). The distribution of perceptions over an ensemble of persons is implemented as a random variable specified by the probability of negative perception, the value of which is set by the control elements of the model interface. The numerical value of the probability equal to 0 corresponds to the case in which all persons positively perceive each other (the numerical value of the random variable is equal to 1, which corresponds to the positive perception of the other person by the individual).
The hierarchy is occupied with operational activity, the degree of intensity of which is set by the external parameter Difficulty. The level of productivity of each manager OAIndex is equal to the level of productivity of the department he leads and is the ratio of the sum of productivity of employees subordinate to the head to the level of complexity of the work Difficulty. An increase in the numerical value of Difficulty leads to a decrease in the OAIndex for all subdivisions of the hierarchy. The managerial meaning of the OAIndex indicator is the percentage of completion of the load specified for the hierarchy as a whole, i.e. the ratio of the actual performance of the structural subdivisions of the hierarchy to the required performance, the level of which is specified by the value of the Difficulty parameter.
…
Epidemic Simulation with Transportation Simulation
FG Econophysics FG Econophysics | Published Monday, March 01, 2021The Episim framework builds upon the established transportation simulation MATSim and is capable of tracking agents’ movements within a network and thus computing infection chains. Several characteristics of the virus and the environment can be parametred, whilst the infection dynamics is computed based upon a compartment model. The spread of the virus can be mitigated by restricting the agents’ activity in certain places.
MedLanD Modeling Laboratory
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Isaac Ullah Gary Mayer Hessam Sarjoughian Helena Mitasova | Published Friday, May 08, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, December 14, 2017The MML is a hybrid modeling environment that couples an agent-based model of small-holder agropastoral households and a cellular landscape evolution model that simulates changes in erosion/deposition, soils, and vegetation.
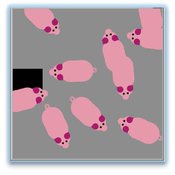
Tail biting behaviour in pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans Iris Jmm Boumans | Published Friday, April 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 14, 2016The model simulates tail biting behaviour in pigs and how they can turn into a biter and/or victim. The effect of a redirected motivation, behavioural changes in victims and preference to bite a lying pig on tail biting can be tested in the model
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
MoPAgrIB: simulating savannah landscape mosaic under shifting cultivation
Nicolas Becu Marc Deconchat Eric Garine Kouami Kokou Christine Raimond | Published Monday, May 27, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2014MoPAgrIB model simulates the movement of cultivated patches in a savannah vegetation mosaic ; how they move and relocate through the landscape, depending on farming practices, population growth, social rules and vegetation growth.
Displaying 10 of 1116 results for "A Flache" clear search