About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1121 results for "Sjoukje A Osinga" clear search
Peer reviewed Zimbabwe Agro-Pastoral Management Model (ZAPMM): Musimboti wevanhu, zvipfuo nezvirimwa
MV Eitzel Solera Kleber Tulio Neves Jon Solera Kenneth B Wilson Abraham Mawere Ndlovu Aaron C Fisher André Veski Oluwasola E Omoju Emmanuel Mhike Hove | Published Tuesday, June 19, 2018This model has been created with and for the researcher-farmers of the Muonde Trust (http://www.muonde.org/), a registered Zimbabwean non-governmental organization dedicated to fostering indigenous innovation. Model behaviors and parameters (mashandiro nemisiyano nedzimwe model) derive from a combination of literature review and the collected datasets from Muonde’s long-term (over 30 years) community-based research. The goals of this model are three-fold (muzvikamu zvitatu):
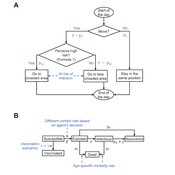
A) To represent three components of a Zimbabwean agro-pastoral system (crops, woodland grazing area, and livestock) along with their key interactions and feedbacks and some of the human management decisions that may affect these components and their interactions.
B) To assess how climate variation (implemented in several different ways) and human management may affect the sustainability of the system as measured by the continued provisioning of crops, livestock, and woodland grazing area.
C) To provide a discussion tool for the community and local leaders to explore different management strategies for the agro-pastoral system (hwaro/nzira yekudyidzana kwavanhu, zvipfuo nezvirimwa), particularly in the face of climate change.
Peer reviewed soslivestock model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral | Published Wednesday, May 28, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025The purpose of this model is to analyze how different management strategies affect the wellbeing, sustainability and resilience of an extensive livestock system under scenarios of climate change and landscape configurations. For this purpose, it simulates one cattle farming system, in which agents (cattle) move through the space using resources (grass). Three farmer profiles are considered: 1) a subsistence farmer that emphasizes self-sufficiency and low costs with limited attention to herd management practices, 2) a commercial farmer focused on profit maximization through efficient production methods, and 3) an environmental farmer that prioritizes conservation of natural resources and animal welfare over profit maximization. These three farmer profiles share the same management strategies to adapt to climate and resource conditions, but differ in their goals and decision-making criteria for when, how, and whether to implement those strategies. This model is based on the SequiaBasalto model (Dieguez Cameroni et al. 2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015), replicated in NetLogo by Soler-Navarro et al. (2023).
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each step begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of animals according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. Animals can be supplemented by the farmer in case of severe drought. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. This updated grass height value becomes the starting grass height for the next day. Cows then move to the next area with the highest grass height. After that, cattle prices are updated and cattle sales are held on the first day of fall. In the event of a severe drought, special sales are held. Finally, at the end of the day, the farm balance and the farmer’s effort are calculated.
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
Managing Connectivity: insights from modelling species interactions accross multiple scales in an idealized landscape
Marco Janssen Michael Schoon Jacopo A. Baggio Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, October 01, 2012 | Last modified Monday, January 20, 2014The model objective’s is to explore the management choice set to uncover which subsets of strategies are most effective at maximizing species coexistence on a fragmented landscape.
A Model of the Gender Cliff in the Relative Contribution to the Household Income
André Grow Jan Van Bavel | Published Wednesday, December 18, 2019In Western countries, the distribution of relative incomes within marriages tends to be skewed in a remarkable way. Husbands usually do not only earn more than their female partners, but there also is a striking discontinuity in their relative contributions to the household income at the 50/50 point: many wives contribute just a bit less than or as much as their husbands, but few contribute more. Our model makes it possible to study a social mechanism that might create this ‘cliff’: women and men differ in their incomes (even outside marriage) and this may differentially affect their abilities to find similar- or higher-income partners. This may ultimately contribute to inequalities within the households that form. The model and associated files make it possible to assess the merit of this mechanism in 27 European countries.
Peer reviewed A Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE)-informed ABM for pedestrian evacuation in different constricted spaces
Jiaqi Ge Yiyu Wang Alexis Comber | Published Wednesday, October 11, 2023This BNE-informed ABM ultimately aims to provide a more realistic description of complicated pedestrian behaviours especially in high-density and life-threatening situations. Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) was adopted to reproduce interactive decision-making process among rational and game-playing agents. The implementations of 3 behavioural models, which are Shortest Route (SR) model, Random Follow (RF) model, and BNE model, make it possible to simulate emergent patterns of pedestrian behaviours (e.g. herding and self-organised queuing behaviours, etc.) in emergency situations.
According to the common features of previous mass trampling accidents, a series of simulation experiments were performed in space with 3 types of barriers, which are Horizontal Corridors, Vertical Corridors, and Random Squares, standing for corridors, bottlenecks and intersections respectively, to investigate emergent behaviours of evacuees in varied constricted spatial environments. The output of this ABM has been available at https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/9v4byyvgxh/1.
Models associated with paper entitled "Polarization in Social Media: A Virtual Worlds-Based Approach"
Sven Banisch Dennis Jacob | Published Thursday, June 22, 2023This model contains MATLAB code describing the virtual worlds framework used in the paper entitled “Polarization in Social Media: A Virtual Worlds-Based Approach.” The parent directory contains driver code for replicating results from the paper. Additionally, the source code is structured by three directories:
- Data Structures: Contains classes and objects used in the code, such as the virtualWorlds.m
- Metrics: Contains code which computes metrics, such as congruentLinks.m
- Visualization: Contains code for generating pictures and plots, such as drawSystemState.m
…
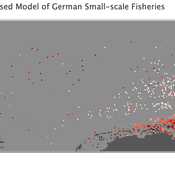
Peer reviewed Viable North Sea (ViNoS): A NetLogo Agent-based Model of German Small-scale Fisheries
Wolfgang Nikolaus Probst Jieun Seo Jürgen Scheffran Carsten Lemmen Sascha Hokamp Verena Mühlberger Serra Örey | Published Thursday, May 25, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 05, 2023Viable North Sea (ViNoS) is an Agent-based Model of the German North Sea Small-scale Fisheries in a Social-Ecological Systems framework focussing on the adaptive behaviour of fishers facing regulatory, economic, and resource changes. Small-scale fisheries are an important part both of the cultural perception of the German North Sea coast and of its fishing industry. These fisheries are typically family-run operations that use smaller boats and traditional fishing methods to catch a variety of bottom-dwelling species, including plaice, sole, and brown shrimp. Fisheries in the North Sea face area competition with other uses of the sea – long practiced ones like shipping, gas exploration and sand extractions, and currently increasing ones like marine protection and offshore wind farming. German authorities have just released a new maritime spatial plan implementing the need for 30% of protection areas demanded by the United Nations High Seas Treaty and aiming at up to 70 GW of offshore wind power generation by 2045. Fisheries in the North Sea also have to adjust to the northward migration of their established resources following the climate heating of the water. And they have to re-evaluate their economic balance by figuring in the foreseeable rise in oil price and the need for re-investing into their aged fleet.
Peer reviewed Family Herd Demography
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Rebecca Garabed Abigail Buffington | Published Monday, August 15, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, January 06, 2018The model examines the dynamics of herd growth in African pastoral systems. We used it to examine the role of scale (herd size) stochasticity (in mortality, fertility, and offtake) on herd growth.
An Agent-Based Model of Insurance Customer Behaviour with Word of Mouth Network in C#
Rei England Iqbal Owadally Douglas Wright | Published Friday, March 04, 2022This is an agent-based model with two types of agents: customers and insurers. Insurers are price-takers who choose how much to spend on their service quality, and customers evaluate insurers based on premium, brand preference, and their perceived service quality. Customers are also connected in a small-world network and may share their opinions with their network.
The ABM contains two types of agents: insurers and customers. These act within the environment of a motor insurance market. At each simulation, the model undergoes the following steps:
- Network generation: At the start of the simulation, the model generates a small world network of social links between the customers, and randomly assigns each customer to an initial insurer ...
Displaying 10 of 1121 results for "Sjoukje A Osinga" clear search