About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 191 results decision clear search
Agent-Based Model of a Circular Food Packaging Ecosystem to assess Packaging Waste Dynamics
Annoek Reitsema | Published Friday, October 11, 2024Reducing packaging waste is a critical challenge that requires organizations to collaborate within circular ecosystems, considering social, economic, and technical variables like decision-making behavior, material prices, and available technologies. Agent-Based Modeling (ABM) offers a valuable methodology for understanding these complex dynamics. In our research, we have developed an ABM to explore circular ecosystems’ potential in reducing packaging waste, using a case study of the Dutch food packaging ecosystem. The model incorporates three types of agents—beverage producers, packaging producers, and waste treaters—who can form closed-loop recycling systems.
Beverage Producer Agents: These agents represent the beverage company divided into five types based on packaging formats: cans, PET bottles, glass bottles, cartons, and bag-in-boxes. Each producer has specific packaging demands based on product volume, type, weight, and reuse potential. They select packaging suppliers annually, guided by deterministic decision styles: bargaining (seeking the lowest price) or problem-solving (prioritizing high recycled content).
Packaging Producer Agents: These agents are responsible for creating packaging using either recycled or virgin materials. The model assumes a mix of monopolistic and competitive market situations, with agents calculating annual material needs. Decision styles influence their choices: bargaining agents compare recycled and virgin material costs, while problem-solving agents prioritize maximum recycled content. They calculate recycled content in packaging and set prices accordingly, ensuring all produced packaging is sold within or outside the model.
…
Peer reviewed Behavior changes through influence
Daria Soboleva | Published Friday, August 30, 2024The model is designed to simulate the behavior and decision-making processes of individuals (agents) in a social network. It aims to represent the changes in individual probability to take any action based on changes in attributes. The action is anything that can be reasonably influenced by the three influencing methods implemented in this model: peer pressure, social media, and state campaigns, and for which the user has a decision-making model. The model is implemented in the multi-agent programmable environment NetLogo 6.3.0.
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Insight into Eco-Choices: Simulating the Fast Fashion Shift
Daria Soboleva Angel Sánchez | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2024 | Last modified Wednesday, June 11, 2025The present model was created and used for the study titled ``Agent-Based Insight into Eco-Choices: Simulating the Fast Fashion Shift.” The model is implemented in the multi-agent programmable environment NetLogo 6.3.0. The model is designed to simulate the behavior and decision-making processes of individuals (agents) in a social network. It focuses on how agents interact with their peers, social media, and government campaigns, specifically regarding their likelihood to purchase fast fashion.
Team Structure and Task Performance
Davide Secchi Martin Neumann | Published Monday, August 05, 2024This model was designed to study resilience in organizations. Inspired by ethnographic work, it follows the simple goal to understand whether team structure affects the way in which tasks are performed. In so doing, it compares the ‘hybrid’ data-inspired structure with three more traditional structures (i.e. hierarchy, flexible/relaxed hierarchy, and anarchy/disorganization).
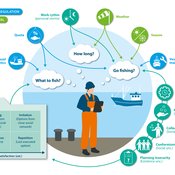
Peer reviewed FISHCODE - FIsheries Simulation with Human COmplex DEcision-making
Birgit Müller Gunnar Dressler Jonas Letschert Christian Möllmann Vanessa Stelzenmüller | Published Monday, August 05, 2024FIsheries Simulation with Human COmplex DEcision-making (FISHCODE) is an agent-based model to depict and analyze current and future spatio-temporal dynamics of three German fishing fleets in the southern North Sea. Every agent (fishing vessel) makes daily decisions about if, what, and how long to fish. Weather, fuel and fish prices, as well as the actions of their colleagues influence agents’ decisions. To combine behavioral theories and enable agents to make dynamic decision, we implemented the Consumat approach, a framework in which agents’ decisions vary in complexity and social engagement depending on their satisfaction and uncertainty. Every agent has three satisfactions and two uncertainties representing different behavioral aspects, i.e. habitual behavior, profit maximization, competition, conformism, and planning insecurity. Availability of extensive information on fishing trips allowed us to parameterize many model parameters directly from data, while others were calibrated using pattern oriented modelling. Model validation showed that spatial and temporal aggregated ABM outputs were in realistic ranges when compared to observed data. Our ABM hence represents a tool to assess the impact of the ever growing challenges to North Sea fisheries and provides insight into fisher behavior beyond profit maximization.
This paper presents an agent-based model to study the dynamics of city-state systems in a constrained environment with limited space and resources. The model comprises three types of agents: city-states, villages, and battalions, where city-states, the primary decision-makers, can build villages for food production and recruit battalions for defense and aggression. In this setting, simulation results, generated through a multi-parameter grid sampling, suggest that risk-seeking strategies are more effective in high-cost scenarios, provided that the production rate is sufficiently high. Also, the model highlights the role of output productivity in defining which strategic preferences are successful in a long-term scenario, with higher outputs supporting more aggressive expansion and military actions, while resource limitations compel more conservative strategies focused on survival and resource conservation. Finally, the results suggest the existence of a non-linear effect of diminishing returns in strategic investments on successful strategies, emphasizing the need for careful resource allocation in a competitive environment.
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
Integrate land use policies into the agent-based model to simulate land use change
Jing Gao | Published Sunday, June 09, 2024This study employs a hierarchical cross-departmental ABM to explore the question: How and to what extent are the land use policies enforced when assessed against the real-world land use pattern? Specifically, two sub-questions are of interest: How can real-world policy interactions be abstracted into the behavior across hierarchical governmental departments in the model? How can the level of enforcement for each land use policy be quantified under these interactions? We build three hierarchical agents—the central level, the local level that incorporates three departments, and the village collective level—with simplified but plausible processes of land use change, with levels of enforcement of different land use policies as key parameters. We calibrate the model using a genetic algorithm to determine those parameters and answer our research question. We further applied the model to simulate potential land use changes and investigate the implications of different policy options. The results are expected to provide insights into the intricate relationships shaping land use processes, contributing to evidence-based decision-making in urban planning and sustainable land use management.
SeaROOTS ABM: Simulating Artificial Hominins Maritime Mobility at Inner Ionian, Greece
Angelos Chliaoutakis | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2024SeaROOTS ABM is a quite generic agent-based modeling system, for simulating and evaluating potential terrestrial and maritime mobility of artificial hominin groups, configured by available archaeological data and hypotheses. Necessary bathymetric, geomorphological and paleoenvironmental data are combined in order to reconstruct paleoshorelines for the study area and produce an archaeologically significant agent environment. Paleoclimatic and archaeological data are incorporated in the ABM in order to simulate maritime crossings and assess the emergent patterns of interaction between human agency and the sea.
SeaROOTS agent-based system includes completely autonomous, utility-based agents (Chliaoutakis & Chalkiadakis 2016), representing artificial hominin groups, with partial knowledge of their environment, for simulating their evolution and potential maritime mobility, utilizing alternative Least Cost Path analysis modeling techniques (Gustas & Supernant 2017, Gravel-Miguel & Wren 2021). Two groups of hominins, Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, are chosen in order to study the challenges and actions employed as a response to the fluctuating sea-levels, as well as probability scenarios with respect to sea-crossings via buoyant vessels (rafting) or the human body itself (swimming). SeaROOTS ABM aims to simulate various scenarios and investigate the degree climatic fluctuations influenced such activities and interactions in the Middle Paleolithic period.
The model focuses on simulating potential terrestrial and maritime routes, explore the interactions and relations between autonomous agents and their environment, as well as to test specific research questions; for example, when and under what conditions would Middle Paleolithic hominins be more likely to attempt a crossing and successfully reach the islands? By which agent type (Sapiens or Neanderthals) and how (e.g. swimming or by sea-vessels) could such short sea crossings be (mostly) attempted, and which (sea) routes were usually considered by the agents? When does a sea-crossing become a choice and when is it a result of forced migration, i.e. disaster- or conflict-induced displacement? Results show that the dynamic marine environment of the Inner Ionian, our case study in this work, played an important role in their decision-making process.
Critical Sustainability Transitions: Relaunching local agriculture after decline (Model code and description)
Pedro Lopez-Merino | Published Tuesday, April 30, 2024This model simulates the dynamics of agricultural land use change, specifically the transition between agricultural and non-agricultural land use in a spatial context. It explores the influence of various factors such as agricultural profitability, path dependency, and neighborhood effects on land use decisions.
The model operates on a grid of patches representing land parcels. Each patch can be in one of two states: exploited (green, representing agricultural land) or unexploited (brown, representing non-agricultural land). Agents (patches) transition between these states based on probabilistic rules. The main factors affecting these transitions are agricultural profitability, path dependency, and neighborhood effects.
-Agricultural Profitability: This factor is determined by the prob-agri function, which calculates the probability of a non-agricultural patch converting to agricultural based on income differences between agriculture and other sectors. -Path Dependency: Represented by the path-dependency parameter, it influences the likelihood of patches changing their state based on their current state. It’s a measure of inertia or resistance to change. -Neighborhood Effects: The neighborhood function calculates the number of exploited (agricultural) neighbors of a patch. This influences the decision of a patch to convert to agricultural land, representing the influence of surrounding land use on the decision-making process.
Displaying 10 of 191 results decision clear search