About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 54 results for "Jesus Rosales-Carreon" clear search
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
PalaeoDiet : Rabbit hunting during the Upper Palaeolithic
Liliana Perez Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke | Published Thursday, October 06, 2022Zooarchaeological evidences indicate that rabbit hunting became prevalent during the Upper Palaeolithic in the Iberian Peninsula.
The purpose of the ABM is to test if warren hunting using nets as a collective strategy can explain the introduction of rabbits in the human diet in the Iberian Peninsula during this period. It is analyzed whether this hunting strategy has an impact on human diet breadth by affecting the relative abundance of other main taxa in the dietary spectrum.
Model validity is measured by comparing simulated diet breadth to the observed diet breadth in the zooarchaeological record.
The agent-based model is explicitly grounded on the Diet Breadth Model (DBM), from the Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT).
…
The Epistemic Role of Diversity in Juries
Aaron Bramson Patrick Grim Daniel J Singer Jiin Jung William J. Berger Bennett Holman | Published Wednesday, August 16, 2023This model is linked to the paper “The Epistemic Role of Diversity in Juries: An Agent-Based Model”. There are many version of this model, but the current version focuses on the role of diversity in whether juries reach correct verdicts. Using this agent-based model, we argue that diversity can play at least four importantly different roles in affecting jury verdicts. (1) Where different subgroups have access to different information, equal representation can strengthen epistemic jury success. (2) If one subgroup has access to particularly strong evidence, epistemic success may demand participation by that group. (3) Diversity can also reduce the redundancy of the information on which a jury focuses, which can have a positive impact. (4) Finally, and most surprisingly, we show that limiting communication between diverse groups in juries can favor epistemic success as well.
ABM Simulation of Transition from Late Longshan Cultures to Early Erlitou Culture
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Within the archeological record for Bronze Age Chinese culture, there continues to be a gap in our understanding of the sudden rise of the Erlitou State from the previous late Longshan chiefdoms. In order to examine this period, I developed and used an agent-based model (ABM) to explore possible socio-politically relevant hypotheses for the gap between the demise of the late Longshan cultures and rise of the first state level society in East Asia. I tested land use strategy making and collective action in response to drought and flooding scenarios, the two plausible environmental hazards at that time. The model results show cases of emergent behavior where an increase in social complexity could have been experienced if a catastrophic event occurred while the population was sufficiently prepared for a different catastrophe, suggesting a plausible lead for future research into determining the life of the time period.
The ABM published here was originally developed in 2016 and its results published in the Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference.
Hollywood Underrepresentation Simulated Causes
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Presented here is a socioeconomic agent-based model (ABM) to examine the Hollywood labor system as a network within a simulated movie labor market based on preferential attachment and compare the findings with 50 co-production ego networks during the 2015 movie year. Using the ABM, I test the role slight individual preference for racial and ethnic similarity within one’s own network at the microlevel and find that it is insufficient to explain the phenomena of racial and ethnic underrepresentation at the macrolevel. The ABM also includes the ability to test alternative explanations, such as overt opportunity loss as a possible explanation.
Endogenous Corruption as a Cellular Automaton
Warren Vierheller | Published Wednesday, June 27, 2018The model explores how corruption may spread endogenously within a closed society by depicting the behavior within a cellular automaton context (CA) between bureaucrats and citizens. Within the model, corruption is characterized as a behavior product dependent upon an individual’s personal disposition towards honesty, rational decisionmaking processes, and neighbors’ behavior.
Human Resource Management Parameter Experimentation Tool
Carmen Iasiello | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, February 25, 2021The agent based model presented here is an explicit instantiation of the Two-Factor Theory (Herzberg et al., 1959) of worker satisfaction and dissatisfaction. By utilizing agent-based modeling, it allows users to test the empirically found variations on the Two-Factor Theory to test its application to specific industries or organizations.
Iasiello, C., Crooks, A.T. and Wittman, S. (2020), The Human Resource Management Parameter Experimentation Tool, 2020 International Conference on Social Computing, Behavioral-Cultural Modeling & Prediction and Behavior Representation in Modeling and Simulation, Washington DC.
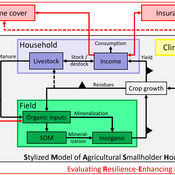
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
Peer reviewed A Picit Jeu: an Agent-Based Model for role-playing game
James Millington Ingrid Vigna | Published Friday, May 24, 2024A Picit Jeu is an agent-based model (ABM) developed as a supporting tool for a role-playing game of the same name. The game is intended for stakeholders involved in land management and fire prevention at a municipality level. It involves four different roles: farmers, forest technicians, municipal administrators and forest private owners. The model aims to show the long-term effects of their different choices about forest and pasture management on fire hazard, letting them test different management strategies in an economically constraining context. It also allows the players to explore different climatic and economic scenarios. A Picit Jeu ABM reproduces the ecological, social and economic characteristics and dynamics of an Alpine valley in north-west Italy. The model should reproduce a primary general pattern: the less players undertake landscape management actions, by thinning and cutting forests or grazing pastures, the higher the probability that a fire will burn a large area of land.
Displaying 10 of 54 results for "Jesus Rosales-Carreon" clear search