About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "M Van Den Hoven" clear search
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
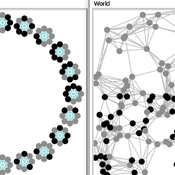
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
Artificial Long House Valley-Black Mesa
Lisa Sattenspiel Amy Warren | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020This model is an extension of the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model developed by the authors (Swedlund et al. 2016; Warren and Sattenspiel 2020). The ALHV model simulates the population dynamics of individuals within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. The present version of the model incorporates features of the ALHV model including realistic age-specific fertility and mortality and, in addition, it adds the Black Mesa environment and population, as well as additional methods to allow migration between the two regions.
As is the case for previous versions of the ALHV model as well as the Artificial Anasazi (AA) model from which the ALHV model was derived (Axtell et al. 2002; Janssen 2009), this version makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original AA model to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the Long House Valley. A new environment and associated methods have been developed for Black Mesa. Productivity estimates from both regions are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Wednesday, February 03, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 11, 2016This Agent-Based model intends to explore the conditions for the emergence and change of land use patterns in Central Asian oases and similar contexts.
Epidemic Simulation with Transportation Simulation
FG Econophysics FG Econophysics | Published Monday, March 01, 2021The Episim framework builds upon the established transportation simulation MATSim and is capable of tracking agents’ movements within a network and thus computing infection chains. Several characteristics of the virus and the environment can be parametred, whilst the infection dynamics is computed based upon a compartment model. The spread of the virus can be mitigated by restricting the agents’ activity in certain places.
Agent-based model of power dynamics in agri-food systems
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, October 27, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, June 12, 2025This is a stylised agent-based model designed to explore the conditions that lead to lock-ins and transitions in agri-food systems.
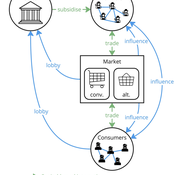
The model represents interactions between four different types of agents: farmers, consumers, markets, and the state. Farmers and consumers are heterogeneous, and at each time step decide whether to trade with one of two market agents: the conventional or alternative. The state agent provides subsidies to the farmers at each time step.
The key emergent outcome is the fraction of trade in each time step that flows through the alternative market agent. This arises from the distributed decisions of farmer and consumer agents. A “sustainability transition” is defined as a shift in the dominant practices (and associated balance of power) towards the alternative paradigm.
…
Simulating the cost of social care in an ageing population
Eric Silverman | Published Thursday, September 16, 2021This model is an agent-based simulation written in Python 2.7, which simulates the cost of social care in an ageing UK population. The simulation incorporates processes of population change which affect the demand for and supply of social care, including health status, partnership formation, fertility and mortality. Fertility and mortality rates are drawn from UK population data, then projected forward to 2050 using the methods developed by Lee and Carter 1992.
The model demonstrates that rising life expectancy combined with lower birthrates leads to growing social care costs across the population. More surprisingly, the model shows that the oft-proposed intervention of raising the retirement age has limited utility; some reductions in costs are attained initially, but these reductions taper off beyond age 70. Subsequent work has enhanced and extended this model by adding more detail to agent behaviours and familial relationships.
The version of the model provided here produces outputs in a format compatible with the GEM-SA uncertainty quantification software by Kennedy and O’Hagan. This allows sensitivity analyses to be performed using Gaussian Process Emulation.
Soy2Grow-ABM-V1
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Monday, January 20, 2025The Soy2Grow ABM aims to simulate the adoption of soybean production in Flanders, Belgium. The model primarily considers two types of agents as farmers: 1) arable and 2) dairy farmers. Each farmer, based on its type, assesses the feasibility of adopting soybean cultivation. The feasibility assessment depends on many interrelated factors, including price, production costs, yield, disease, drought (i.e., environmental stress), social pressure, group formations, learning and skills, risk-taking, subsidies, target profit margins, tolerance to bad experiences, etc. Moreover, after adopting soybean production, agents will reassess their performance. If their performance is unsatisfactory, an agent may opt out of soy production. Therefore, one of the main outcomes to look for in the model is the number of adopters over time.
The main agents are farmers. Generally, factors influencing farmers’ decision-making are divided into seven main areas: 1) external environmental factors, 2) cooperation and learning (with slight differences depending on whether they are arable or dairy farmers), 3) crop-specific factors, 4) economics, 5) support frameworks, 6) behavioral factors, and 7) the role of mobile toasters (applicable only to dairy farmers).
Moreover, factors not only influence decision-making but also interact with each other. Specifically, external environmental factors (i.e., stress) will result in lower yield and quality (protein content). The reducing effect, identified during participatory workshops, can reach 50 %. Skills can grow and improve yield; however, their growth has a limit and follows different learning curves depending on how individualistic a farmer is. During participatory workshops, it was identified that, contrary to cooperative farmers, individualistic farmers may learn faster and reach their limits more quickly. Furthermore, subsidies directly affect revenues and profit margins; however, their impact may disappear when they are removed. In the case of dairy farmers, mobile toasters play an important role, adding toasting and processing costs to those producing soy for their animal feed consumption.
Last but not least, behavioral factors directly influence the final adoption decision. For example, high risk-taking farmers may adopt faster, whereas more conservative farmers may wait for their neighbors to adopt first. Farmers may evaluate their success based on their own targets and may also consider other crops rather than soy.
Correlated random walk
Thibault Fronville | Published Friday, April 01, 2022 | Last modified Monday, April 25, 2022The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
This model is implemented in python and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
Correlated random walk (Javascript)
Viktoriia Radchuk Uta Berger Thibault Fronville | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
In this script the turning angles (following the Von Mises distribution) are generated based on the the instructions from N. I. Fisher 2011.
This model is implemented in Javascript and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
The Evolution of Cooperation in an Ecological Context
Oyita Udiani | Published Saturday, November 03, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a replication of the altruistic trait selection model described in Pepper & Smuts (2000, 2002).
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "M Van Den Hoven" clear search