About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 990 results for "Chantal van Esch" clear search
Demographic microsimulation for individuals and couples
Sabine Zinn | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015The simulation model conducts fine-grained population projection by specifying life course dynamics of individuals and couples by means of traditional demographic microsimulation and by using agent-based modeling for mate matching.
Agent-Based Simulation for International Tax Compliance
Peter Gerbrands | Published Tuesday, July 18, 2023Country-by-Country Reporting and Automatic Exchange of Information have recently been implemented in European Union (EU) countries. These international tax reforms increase tax compliance in the short term. In the long run, however, taxpayers will continue looking abroad to avoid taxation and, countries, looking for additional revenues, will provide opportunities. As a result, tax competition intensifies and the initial increase in compliance could reverse. To avoid international tax reforms being counteracted by tax competition, this paper suggests bilateral responsive regulation to maximize compliance. This implies that countries would use different tax policy instruments toward other countries, including tax and secrecy havens.
To assess the effectiveness of fully or partially enforce tax policies, this agent based model has been ran many times under different enforcement rules, which influence the perceived enforced- and voluntary compliance, as the slippery-slope model prescribes. Based on the dynamics of this perception and the extent to which agents influence each other, the annual amounts of tax evasion, tax avoidance and taxes paid are calculated over longer periods of time.
The agent-based simulation finds that a differentiated policy response could increase tax compliance by 6.54 percent, which translates into an annual increase of €105 billion in EU tax revenues on income, profits, and capital gains. Corporate income tax revenues in France, Spain, and the UK alone would already account for €35 billion.
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
Simulation of Self-enforcing Agreement in Cooperative Teams
Hang Xiong | Published Friday, April 01, 2016This is an agent-based model of the implementation of the self-enforcing agreement in cooperative teams.
Role of Diversity in Team Performance: the Case of Missing Expertise, an Agent Based Simulations
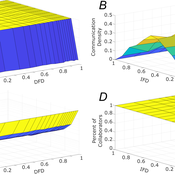
Tamás Kiss | Published Friday, December 29, 2023This ABM simulates problem solving agents as they work on a set of tasks. Each agent has a trait vector describing their skills. Two agents might form a collaboration if their traits are similar enough. Tasks are defined by a component vector. Agents work on tasks by decreasing tasks’ component vectors towards zero.
The simulation generates agents with given intrapersonal functional diversity (IFD), and dominant function diversity (DFD), and a set of random tasks and evaluates how agents’ traits influence their level of communication and the performance of a team of agents.
Modeling results highlight the importance of the distributions of agents’ properties forming a team, and suggests that for a thorough description of management teams, not only diversity measures based on individual agents, but an aggregate measure is also required.
…
Youth and their Artificial Social Environmental Risk and Promotive Scores (Ya-TASERPS)
JoAnn Lee | Published Wednesday, July 07, 2021 | Last modified Friday, February 24, 2023Risk assessments are designed to measure cumulative risk and promotive factors for delinquency and recidivism, and are used by criminal and juvenile justice systems to inform sanctions and interventions. Yet, these risk assessments tend to focus on individual risk and often fail to capture each individual’s environmental risk. This agent-based model (ABM) explores the interaction of individual and environmental risk on the youth. The ABM is based on an interactional theory of delinquency and moves beyond more traditional statistical approaches used to study delinquency that tend to rely on point-in-time measures, and to focus on exploring the dynamics and processes that evolve from interactions between agents (i.e., youths) and their environments. Our ABM simulates a youth’s day, where they spend time in schools, their neighborhoods, and families. The youth has proclivities for engaging in prosocial or antisocial behaviors, and their environments have likelihoods of presenting prosocial or antisocial opportunities.
Swidden farming by individual households
C Michael Barton | Published Sunday, April 27, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Swidden Farming is designed to explore the dynamics of agricultural land management strategies.
The Effectiveness of Image-Scoring Under Different Ecological Conditions
G M Leighton | Published Monday, January 06, 2014The set of models test how receivers ability to accurately rank signalers under various ecological and behavioral contexts.
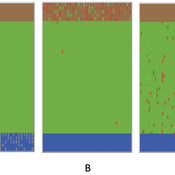
This project attempts to model how social media platforms recommend a user followers based on their interests, and how those individual interests change as a result of the influences from those they follow/are followed by.
We have three types of users on the platform:
Consumers (🔴), who update their interests based on who they’re following.
Creators (⬛), who update their interests based on who’s following them.
…
GenoScope
Kristin Crouse | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2024 | Last modified Wednesday, April 09, 2025GenoScope is a modular agent-based model designed to simulate how cells respond to environmental stressors or other treatment conditions across species. Genes, treatment conditions, and cell physiology outcomes are represented as interacting agents that influence each other’s behavior over time. Rather than imposing fixed interaction rules, GenoScope initializes with randomized regulatory logic and calibrates rule sets based on empirical data. Calibration is grounded in a common-garden experiment involving 16 mammalian species—including humans, dolphins, bats, and camels—exposed to varying levels of temperature, glucose, and oxygen. This comparative approach enables the identification of mechanisms by which animal cells achieve robustness under extreme environmental conditions.
Displaying 10 of 990 results for "Chantal van Esch" clear search