About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 258 results for "Marlies Bitter-Rijpkema" clear search
Peer reviewed Monogamous Reproduction in Small Populations and the Enforcement of the Incest Taboo
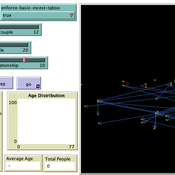
Ian Stuart | Published Wednesday, January 18, 2023This program was developed to simulate monogamous reproduction in small populations (and the enforcement of the incest taboo).
Every tick is a year. Adults can look for a mate and enter a relationship. Adult females in a Relationship (under the age of 52) have a chance to become pregnant. Everyone becomes not alive at 77 (at which point people are instead displayed as flowers).
User can select a starting-population. The starting population will be adults between the ages of 18 and 42.
…
Talent vs Luck: the role of randomness in success and failure
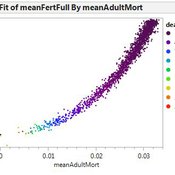
Alessandro Pluchino Alessio Emanuele Biondo Andrea Rapisarda | Published Monday, July 16, 2018The largely dominant meritocratic paradigm of highly competitive Western cultures is rooted on the belief that success is due mainly, if not exclusively, to personal qualities such as talent, intelligence, skills, smartness, efforts, willfulness, hard work or risk taking. Sometimes, we are willing to admit that a certain degree of luck could also play a role in achieving significant material success. But, as a matter of fact, it is rather common to underestimate the importance of external forces in individual successful stories. It is very well known that intelligence (or, more in general, talent and personal qualities) exhibits a Gaussian distribution among the population, whereas the distribution of wealth - often considered a proxy of success - follows typically a power law (Pareto law), with a large majority of poor people and a very small number of billionaires. Such a discrepancy between a Normal distribution of inputs, with a typical scale (the average talent or intelligence), and the scale invariant distribution of outputs, suggests that some hidden ingredient is at work behind the scenes. In a recent paper, with the help of this very simple agent-based model realized with NetLogo, we suggest that such an ingredient is just randomness. In particular, we show that, if it is true that some degree of talent is necessary to be successful in life, almost never the most talented people reach the highest peaks of success, being overtaken by mediocre but sensibly luckier individuals. As to our knowledge, this counterintuitive result - although implicitly suggested between the lines in a vast literature - is quantified here for the first time. It sheds new light on the effectiveness of assessing merit on the basis of the reached level of success and underlines the risks of distributing excessive honors or resources to people who, at the end of the day, could have been simply luckier than others. With the help of this model, several policy hypotheses are also addressed and compared to show the most efficient strategies for public funding of research in order to improve meritocracy, diversity and innovation.
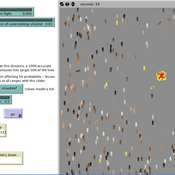
Active Shooter: An Agent-Based Model of Unarmed Resistance
William Kennedy Tom Briggs | Published Thursday, December 29, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, April 04, 2017A NetLogo ABM developed to explore unarmed resistance to an active shooter. The landscape is a generalized open outdoor area. Parameters enable the user to set shooter armament and control for assumptions with regard to shooter accuracy.
Seascapes of the Unreal: Using Agent Based Modeling to Examine Traditional Coast Salish Maritime Mobility
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Friday, December 22, 2023Non-traditional tools and mediums can provide unique methodological and interpretive opportunities for archaeologists. In this case, the Unreal Engine (UE), which is typically used for games and media, has provided a powerful tool for non-programmers to engage with 3D visualization and programming as never before. UE has a low cost of entry for researchers as it is free to download and has user-friendly “blueprint” tools that are visual and easily extendable. Traditional maritime mobility in the Salish Sea is examined using an agent-based model developed in blueprints. Focusing on the sea canoe travel of the Straits Salish northwestern Washington State and southwest British Columbia. This simulation integrates GIS data to assess travel time between Coast Salish archaeological village locations and archaeologically represented resource gathering areas. Transportation speeds informed by ethnographic data were used to examine travel times for short forays and longer inter-village journeys. The results found that short forays tended to half day to full day trips when accounting for resource gathering activities. Similarly, many locations in the Salish Sea were accessible in long journeys within two to three days, assuming fair travel conditions. While overall transportation costs to reach sites may be low, models such as these highlight the variability in transport risk and cost. The integration of these types of tools, traditionally used for entertainment, can increase the accessibility of modeling approaches to researchers, be expanded to digital storytelling, including aiding in the teaching of traditional ecological knowledge and placenames, and can have wide applications beyond maritime archaeology.
This is v0.01 of a UE5.2.1 agent based model.
A model to explore the link between the gender-gap reversal in education and relative divorce risks
Jan Van Bavel Christine Schnor André Grow | Published Thursday, June 30, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 13, 2017This model explores a social mechanism that links the reversal of the gender gap in education with changing patterns in relative divorce risks in 12 European countries.
FilterBubbles_in_Carley1991
Benoît Desmarchelier | Published Wednesday, May 21, 2025The model is an extension of: Carley K. (1991) “A theory of group stability”, American Sociological Review, vol. 56, pp. 331-354.
The original model from Carley (1991) works as follows:
- Agents know or ignore a series of knowledge facts;
- At each time step, each agent i choose a partner j to interact with at random, with a probability of choice proportional to the degree of knowledge facts they have in common.
- Agents interact synchronously. As such, interaction happens only if the partnert j is not already busy interacting with someone else.
…
ForagerNet3_Demography: A Non-Spatial Model of Hunter-Gatherer Demography
Andrew White | Published Thursday, October 17, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 17, 2013ForagerNet3_Demography is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. Key methods represent birth, death, and marriage. The dependency ratio is an imporant variable in many economic decisions embedded in the methods.
ForagerNet3_Demography_V2
Andrew White | Published Thursday, February 13, 2014ForagerNet3_Demography_V2 is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. This version (developed from FN3D_V1) contains code for calculating the ratio of old to young adults (the “OY ratio”) in the living and dead populations.
The Travel-tour case study
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Françoise Adreit Joseph El Gemayel | Published Sunday, May 19, 2013 | Last modified Friday, June 14, 2013This model describes and analyses the Travel-Tour Case study.
In-group favoritism due to friend selection strategies based on fixed tag and within-group reputation
Yutaka Nakai | Published Friday, March 28, 2014 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014An agent-based model simulates emergence of in-group favoritism. Agents adopt friend selection strategies using an invariable tag and reputations meaning how cooperative others are to a group. The reputation can be seen as a kind of public opinion.
Displaying 10 of 258 results for "Marlies Bitter-Rijpkema" clear search