About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 32 results for "Christhophe Sibertin-Blanc" clear search
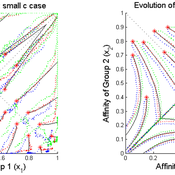
Affinity/Hostility in Divided Communities
Christopher Thron | Published Friday, January 22, 2016Agent-based model of intergroup conflict in divided communities.
Agent-based simulation of small group decision-making under no communication
Christopher Poile | Published Thursday, May 26, 2016A computational model of a classic small group study by Alex Bavelas. This computational model was designed to explore the difficulty in translating a seemingly simple real-world experiment into a computational model.
Pollution-development Tradeoffs in Nigeria--an Agent-based Model
Christopher Thron | Published Thursday, June 03, 2021Like many developing countries, Nigeria is faced with a number of tradeoffs that pit rapid economic development against environmental preservation. Environmentally sustainable, “green” economic development is slower, more costly, and more difficult than unrestricted, unregulated economic growth. The mathematical model that we develop in this code suggests that widespread public awareness of environmental issues is insufficient to prevent the tendency towards sacrificing the environment for the sake of growth. Even if people have an understanding of negative impacts and always choose to act in their own self-interest, they may still act collectively in such a way as to bring down the quality of life for the entire society. We conclude that additional actions must be taken besides raising public awareness of the environmental problem.
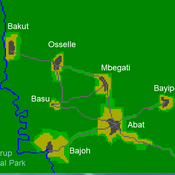
A stylized scale model to codesign with villagers an agent-based model of bushmeat hunting in the periphery of Korup National Park (Cameroon)
Agent-based model of WiFi tracking system in urban environment
Christopher Thron Khoi Tran | Published Friday, April 21, 2017This code simulates the WiFi user tracking system described in: Thron et al., “Design and Simulation of Sensor Networks for Tracking Wifi Users in Outdoor Urban Environments”. Testbenches used to create the figures in the paper are included.
Hegmon's Model of Sharing
Sean Bergin | Published Thursday, May 02, 2013The purpose of Hegmon’s Sharing model is to develop an understanding of the effect sharing strategies have on household survival.
Peer reviewed Torsten Hägerstrand’s Spatial Innovation Diffusion Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a replication of Torsten Hägerstrand’s 1965 model–one of the earliest known calibrated and validated simulations with implicit “agent based” methodology.
The Cardial Spread Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 29, 2017 | Last modified Monday, February 04, 2019The purpose of this model is to provide a platform to test and compare four conceptual models have been proposed to explain the spread of the Impresso-Cardial Neolithic in the west Mediterranean.
Geographic Expansion Model (GEM)
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, February 28, 2020The purpose of this model is to explore the importance of geographic factors to the settlement choices of early Neolithic agriculturalists. In the model, each agriculturalist spreads to one of the best locations within a modeler specified radius. The best location is determined by choosing either one factor such as elevation or slope; or by ranking geographic factors in order of importance.
Peer reviewed TRANSOPE: a multi-agent model to simulate outsourcing networks in road freight transport.
Aitor Salas-Peña Blanca Rosa Cases Gutiérrez | Published Friday, October 21, 2022A road freight transport (RFT) operation involves the participation of several types of companies in its execution. The TRANSOPE model simulates the subcontracting process between 3 types of companies: Freight Forwarders (FF), Transport Companies (TC) and self-employed carriers (CA). These companies (agents) form transport outsourcing chains (TOCs) by making decisions based on supplier selection criteria and transaction acceptance criteria. Through their participation in TOCs, companies are able to learn and exchange information, so that knowledge becomes another important factor in new collaborations. The model can replicate multiple subcontracting situations at a local and regional geographic level.
The succession of n operations over d days provides two types of results: 1) Social Complex Networks, and 2) Spatial knowledge accumulation environments. The combination of these results is used to identify the emergence of new logistics clusters. The types of actors involved as well as the variables and parameters used have their justification in a survey of transport experts and in the existing literature on the subject.
As a result of a preferential selection process, the distribution of activity among agents shows to be highly uneven. The cumulative network resulting from the self-organisation of the system suggests a structure similar to scale-free networks (Albert & Barabási, 2001). In this sense, new agents join the network according to the needs of the market. Similarly, the network of preferential relationships persists over time. Here, knowledge transfer plays a key role in the assignment of central connector roles, whose participation in the outsourcing network is even more decisive in situations of scarcity of transport contracts.
Displaying 10 of 32 results for "Christhophe Sibertin-Blanc" clear search