About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 314 results for "Michael D. Slater" clear search
Neolithic Spread Model Version 1.0
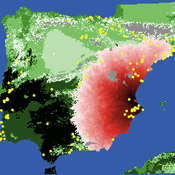
Sean Bergin Salvador Pardo Gordo Joan Bernabeu Auban Michael Barton | Published Thursday, December 11, 2014 | Last modified Monday, December 31, 2018This model simulates different spread hypotheses proposed for the introduction of agriculture on the Iberian peninsula. We include three dispersal types: neighborhood, leapfrog, and ideal despotic distribution (IDD).
Peer reviewed Mission Cattle
Isaac Ullah | Published Monday, December 15, 2025The model examines cattle herd dynamics on a patchy grassland subject to two exogenous pressures: periodic raiding events that remove animals and scheduled management culling that can target males and/or females. It is intended for comparative experiments on how raiding frequency, culling schedules, vegetation dynamics, and life-history parameters interact to shape herd persistence. The model was specifically designed to test the scenario of cattle herding in the arid grasslands of southern Arizona and northern Sonora during the mission period (late 17th through late 18th centuries, CE). In this period, herds were locally managed by Spanish mission personnel and local O’odham groups. Herds were culled mostly for local consumption of meat, hides, and tallow, but the mission herds were often targets for raiding by neighboring groups. The main purpose of the model is to examine herd dynamics in a seasonally variable, arid environment where herds are subject to both intentional internal harvest (culling) and external harvest (raiding).
DARTS: modelling effects of shocks on global, regional, urban and rural food security
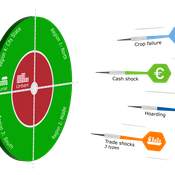
Geerten Hengeveld Hubert Fonteijn Pepijn van Oort | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2024Food trade networks represent a complex system where food is periodically produced in different regions of the world. Food is continuously stocked and traded. Food security in a globalised world is vulnerable to shocks. We present DARTS, a new agent based model that models monthly dynamics of food production, trade, stocking, consumption and food security for different interconnected world regions and a city state. Agents in different regions differ in their harvest seasons, wealth (rich and poor), degree of urbanisation and connection to domestic and global markets. DARTS was specifically designed to model direct and indirect effects of shocks in the food system. We introduce a new typology of 6 distinct shock types and analyse their impact on food security, modelling local and global effects and short term and longer term effects. An second important scientific novelty of the model is that DARTS can also model indirect effects of shocks (cascading in space and in time, lag effects due to trade and food stock buffering). A third important scientific novelty of the model is its’ capability of modelling food security at different scales, in which the rural/urban divide and differences in (intra-annually varying) production and trade connections play a key role. At the time of writing DARTS is yet insufficiently parameterised for accurate prediction for real world regions and cities. Simulations for a hypothetical in silico world with 3 regions and a city state show that DARTS can reproduce rich and complex dynamics with analogues in the real world. The scientific interest is more on deepening insight in process dynamics and chains of events that lead to ultimate shock effects on food security.
Agent-based model of sexual partnership
Andrea Knittel | Published Monday, December 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In this model agents meet, evaluate one another, decide whether or not to date, if and when to become sexual partners, and when to break up.
CHAAHK: a Spatial Simulation of the Maya Elevated Core Region
Alex Kara | Published Tuesday, December 04, 2018 | Last modified Thursday, September 26, 2019This thesis presents an abstract spatial simulation model of the Maya Central Lowlands coupled human and natural system from 1000 BCE to the present day. It’s name is the Climatically Heightened but Anothropogenically Achieved Historical Kerplunk model (CHAAHK). The simulation features features virtual human groups, population centers, transit routes, local resources, and imported resources. Despite its embryonic state, the model demonstrates how certain anthropogenic characteristics of a landscape can interact with externally induced trauma and result in a prolonged period of relative sociopolitical uncomplexity. Analysis of batch simulation output suggests decreasing empirical uncertainties about ancient wetland modification warrants more investment. This first submission of CHAAHK’s code represents the simulation’s implementation that was featured in the author’s master’s thesis.
Protein 2.0: An Agent-Based Model for Simulating Norway’s Protein Sector Under Carbon Pricing and the Emergence of Cultivated Proteins
Gary Polhill Nick Roxburgh Rob J.F. Burton Klaus Mittenzwei | Published Thursday, May 08, 2025Protein 2.0 is a systems model of the Norwegian protein sector designed to explore the potential impacts of carbon taxation and the emergence of cultivated meat and dairy technologies. The model simulates production, pricing, and consumption dynamics across conventional and cultivated protein sources, accounting for emissions intensity, technological learning, economies of scale, and agent behaviour. It assesses how carbon pricing could alter the competitiveness of conventional beef, lamb, pork, chicken, milk, and egg production relative to emerging cultivated alternatives, and evaluates the implications for domestic production, emissions, and food system resilience. The model provides a flexible platform for exploring policy scenarios and transition pathways in protein supply. Further details can be found in the associated publication.
Agent-based model for centralized student admission process
Connie Wang Shu-Heng Chen Bin-Tzong Chi | Published Wednesday, November 04, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, March 06, 2019This model is to match students and schools using real-world student admission mechanisms. The mechanisms in this model are serial dictatorship, deferred acceptance, the Boston mechanism, Chinese Parallel, and the Taipei mechanism.
CPNorm
Ruth Meyer | Published Sunday, June 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, June 13, 2017CPNorm is a model of a community of harvesters using a common pool resource where adhering to the optimal extraction level has become a social norm. The model can be used to explore the robustness of norm-driven cooperation in the commons.
Exploring Transitions towards Sustainable Construction
Jesus Rosales-Carreon César García-Díaz | Published Wednesday, October 30, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, January 31, 2015This model illustrates actor interaction in the construction sector, according to information gathered in NL. It offers a simple frame to represent diverse interests, interdependencies and effects on the number of built sustainable houses.
A Model to Unravel the Complexity of Rural Food Security
Stefano Balbi Samantha Dobbie | Published Monday, August 22, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018An ABM to simulate the behaviour of households within a village and observe the emerging properties of the system in terms of food security. The model quantifies food availability, access, utilisation and stability.
Displaying 10 of 314 results for "Michael D. Slater" clear search