About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 126 results decision-making clear search
The Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice
Guido Fioretti | Published Saturday, June 22, 2013We reconstruct Cohen, March and Olsen’s Garbage Can model of organizational choice as an agent-based model. We add another means for avoiding making decisions: buck-passing difficult problems to colleagues.
Implementation of 'satisficing’ as a model for farmers’ decision-making in an agent-based model of groundwater over-exploitation
Marvin Nebel | Published Monday, May 20, 2013This model uses ’satisficing’ as a model for farmers’ decision making to learn about influences of alternative decision-making models on simulation results and to exemplify a way to transform a rather theoretical concept into a feasible decision-making model for agent-based farming models.
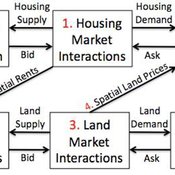
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Enhancing recycling of construction materials; an agent based model with empirically based decision parameters
Igor Nikolic Claudia Binder Christof Knoeri Hans-Joerg Althaus | Published Sunday, October 21, 2012 | Last modified Monday, June 09, 2014This model allows for analyzing the most efficient levers for enhancing the use of recycled construction materials, and the role of empirically based decision parameters.
A land-use model to illustrate ambiguity in design
Julia Schindler | Published Monday, October 15, 2012 | Last modified Friday, January 13, 2017This is an agent-based model that allows to test alternative designs for three model components. The model was built using the LUDAS design strategy, while each alternative is in line with the strategy. Using the model, it can be shown that alternative designs, though built on the same strategy, lead to different land-use patterns over time.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
Irrigation game
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, July 23, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Irrigation game calibrated on experimental data
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross | Published Friday, December 30, 2011 | Last modified Friday, November 21, 2014We present an agent-based model that maps out and simulates the processes by which individuals within ecological restoration organizations communicate and collectively make restoration decisions.
Agent-based model of sexual partnership
Andrea Knittel | Published Monday, December 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In this model agents meet, evaluate one another, decide whether or not to date, if and when to become sexual partners, and when to break up.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
Displaying 10 of 126 results decision-making clear search