About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 166 results for "Bennett Holman" clear search
TRUE GRASP (Tree Recruitment Under Exotic GRAsses in a Savanna-Pineland)
is a socio-ecological agent-based model (ABM) and role playing game (RPG) for farmers and other stakeholders involved in rural landscape planning.
The purpose of this model is to allow actors to explore the individual and combined effects - as well as tradeoffs - of three methods of controlling exotic grasses in pine savannas: fire, weeding, and grazing cattle.
Design of TRUE GRASP is based on 3 years of socio-ecological fieldwork in a human-induced pine savanna in La Sepultura Biosphere Reserve (SBR) in the Mexican state of Chiapas. In this savanna, farmers harvest resin from Pinus oocarpa, which is used to produce turpentine and other products. However, long term persistence of this activity is jeopardized by low tree recruitment due to exotic tall grass cover in the forest understory (see Braasch et al., 2017). The TRUE GRASP model provides the user with different management strategies for controlling exotic grass cover and avoiding possible regime shifts, which in the case of the SBR would jeopardize resin harvesting.
BEGET Classic
Kristin Crouse | Published Monday, November 11, 2019 | Last modified Monday, November 25, 2019BEGET Classic includes previous versions used in the classroom and for publication. Please check out the latest version of B3GET here, which has several user-friendly features such as directly importing and exporting genotype and population files.
The classic versions of B3GET include: version one and version three were used in undergraduate labs at the University of Minnesota to demonstrate principles in primate behavioral ecology; version two first demonstrated proof of concept for creating virtual biological organisms using decision-vector algorithms; version four was presented at the 2017 annual meeting at the American Association of Physical Anthropologists; version five was presented in a 2019 publication from the Journal of Human Evolution (Crouse, Miller, and Wilson, 2019).
A simple emulation-based computational model
Carlos M Fernández-Márquez Francisco J Vázquez | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 05, 2019Emulation is one of the simplest and most common mechanisms of social interaction. In this paper we introduce a descriptive computational model that attempts to capture the underlying dynamics of social processes led by emulation.
Societal Simulator v203
Tim Gooding | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, November 28, 2014Designed to capture the evolutionary forces of global society.
Peer reviewed Urban Transport Mode Choices
Kathleen Salazar -Serna Lorena Cadavid Carlos Franco | Published Thursday, May 22, 2025The model represents urban commuters’ transport mode choices among cars, public transit, and motorcycles—a mode highly prevalent in developing countries. Using an agent-based modeling approach, it simulates transport dynamics and serves as a testbed for evaluating policies aimed at improving mobility.
The model simulates an ecosystem of human agents who decide, at each time step, which mode of transportation to use for commuting to work. Their decision is based on a combination of personal satisfaction with their most recent journey—evaluated across a vector of individual needs—the information they crowdsource from their social network, and their personal uncertainty regarding trying new transport options.
Agents are assigned demographic attributes such as sex, age, and income level, and are distributed across city neighborhoods according to their socioeconomic status. To represent social influence in decision-making, agents are connected via a scale-free social network topology, where connections are more likely among agents within the same socioeconomic group, reflecting the tendency of individuals to form social ties with similar others.
…
Peer reviewed DogFoxCDVspillover
Aniruddha Belsare Matthew Gompper | Published Thursday, March 16, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, April 04, 2017The purpose of this model is to better understand the dynamics of a multihost pathogen in two host system comprising of high densities of domestic hosts and sympatric wildlife hosts susceptible to the pathogen.
OMOLAND-CA: An Agent-Based Modeling of Rural Households’ Adaptation to Climate Change
Atesmachew Hailegiorgis Andrew Crooks Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, July 25, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, July 10, 2018The purpose of the OMOLAND-CA is to investigate the adaptive capacity of rural households in the South Omo zone of Ethiopia with respect to variation in climate, socioeconomic factors, and land-use at the local level.
An Agent Based Model for implementing a double auction financial market
Annalisa Fabretti | Published Thursday, April 14, 2016The model implements a double auction financial markets with two types of agents: rational and noise. The model aims to study the impact of different compensation structure on the market stability and market quantities as prices, volumes, spreads.
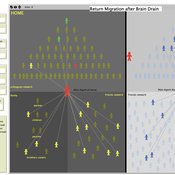
RETURN MIGRATION AFTER BRAIN DRAIN: A SIMULATION APPROACH
Alessandro Pluchino Alessio Emanuele Biondo Andrea Rapisarda | Published Friday, June 21, 2013This model, realized on the NetLogo platform, compares utility levels at home and abroad to simulate agents’ migration and their eventual return. Our model is based on two fundamental individual features, i.e. risk aversion and initial expectation, which characterize the dynamics of different agents according to the evolution of their social contacts.
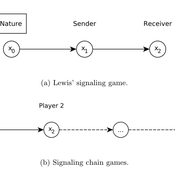
Lewis' Signaling Chains
Giorgio Gosti | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 03, 2015Signaling chains are a special case of Lewis’ signaling games on networks. In a signaling chain, a sender tries to send a single unit of information to a receiver through a chain of players that do not share a common signaling system.
Displaying 10 of 166 results for "Bennett Holman" clear search