About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1108 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search
A Modelling4All/NetLogo model of the Spanish Flu Pandemic
Ken Kahn | Published Monday, August 05, 2013 | Last modified Monday, August 05, 2013A global model of the 1918-19 Influenza Pandemic. It can be run to match history or explore counterfactual questions about the influence of World War I on the dynamics of the epidemic. Explores two theories of the location of the initial infection.
Peak-seeking Adder
Julia Kasmire Janne M Korhonen | Published Tuesday, December 02, 2014 | Last modified Friday, February 20, 2015Continuing on from the Adder model, this adaptation explores how rationality, learning and uncertainty influence the exploration of complex landscapes representing technological evolution.
A Model to Unravel the Complexity of Rural Food Security
Stefano Balbi Samantha Dobbie | Published Monday, August 22, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018An ABM to simulate the behaviour of households within a village and observe the emerging properties of the system in terms of food security. The model quantifies food availability, access, utilisation and stability.
Exploring Urban Shrinkage
Andrew Crooks | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020While the world’s total urban population continues to grow, this growth is not equal. Some cities are declining, resulting in urban shrinkage which is now a global phenomenon. Many problems emerge due to urban shrinkage including population loss, economic depression, vacant properties and the contraction of housing markets. To explore this issue, this paper presents an agent-based model stylized on spatially explicit data of Detroit Tri-county area, an area witnessing urban shrinkage. Specifically, the model examines how micro-level housing trades impact urban shrinkage by capturing interactions between sellers and buyers within different sub-housing markets. The stylized model results highlight not only how we can simulate housing transactions but the aggregate market conditions relating to urban shrinkage (i.e., the contraction of housing markets). To this end, the paper demonstrates the potential of simulation to explore urban shrinkage and potentially offers a means to test polices to alleviate this issue.
Modeling financial networks based on interpersonal trust
Michael Roos Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, November 28, 2013We build a stylized model of a network of business angel investors and start-up entrepreneurs. Decisions are based on trust as a decision making tool under true uncertainty.
Land-Livelihood Transitions
Nicholas Magliocca Daniel G Brown Erle C Ellis | Published Monday, September 09, 2013 | Last modified Friday, September 13, 2013Implemented as a virtual laboratory, this model explores transitions in land-use and livelihood decisions that emerge from changing local and global conditions.
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
Peer reviewed Lithic Raw Material Procurement and Provisioning
Jonathan Paige | Published Friday, March 06, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015This model simulates the lithic raw material use and provisioning behavior of a group that inhabits a permanent base camp, and uses stone tools.
Potato late blight model
Francine Pacilly | Published Friday, April 13, 2018The purpose of the model is to simulate the spatial dynamics of potato late blight to analyse whether resistant varieties can be used effectively for sustainable disease control. The model represents an agricultural landscape with potato fields and data of a Dutch agricultural region is used as input for the model. We simulated potato production, disease spread and pathogen evolution during the growing season (April to September) for 36 years. Since late blight development and crop growth is weather dependent, measured weather data is used as model input. A susceptible and late blight resistant potato variety are distinguished. The resistant variety has a potentially lower yield but cannot get infected with the disease. However, during the growing season virulent spores can emerge as a result of mutations during spore production. This new virulent strain is able to infect the resistant fields, resulting in resistance breakdown. The model shows how disease severity, resistance durability and potato yield are affected by the fraction of fields across a landscape with a disease-resistant potato variety.
Demography, Industry and Residential Choice (DIReC) model
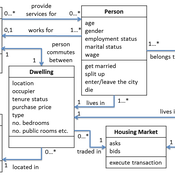
Jiaqi Ge | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2019The integrated and spatially-explicit ABM, called DIReC (Demography, Industry and Residential Choice), has been developed for Aberdeen City and the surrounding Aberdeenshire (Ge, Polhill, Craig, & Liu, 2018). The model includes demographic (individual and household) models, housing infrastructure and occupancy, neighbourhood quality and evolution, employment and labour market, business relocation, industrial structure, income distribution and macroeconomic indicators. DIReC includes a detailed spatial housing model, basing preference models on house attributes and multi-dimensional neighbourhood qualities (education, crime, employment etc.).
The dynamic ABM simulates the interactions between individuals, households, the labour market, businesses and services, neighbourhoods and economic structures. It is empirically grounded using multiple data sources, such as income and gender-age distribution across industries, neighbourhood attributes, business locations, and housing transactions. It has been used to study the impact of economic shocks and structural changes, such as the crash of oil price in 2014 (the Aberdeen economy heavily relies on the gas and oil sector) and the city’s transition from resource-based to a green economy (Ge, Polhill, Craig, & Liu, 2018).
Displaying 10 of 1108 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search