About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1110 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
Sea Bright, NJ Reconstruction of Hurricane Sandy
Kim McEligot | Published Saturday, March 20, 2021 This model implements a combined Protective Action Decision Model (PADM) and Protection Motivation Theory (PAM) model for human decision making regarding hazard mitigations. The model is developed and integrated into the MASON modeling framework. The ABM implements a hind-cast of Hurricane Sandy’s damage to Sea Bright, NJ and homeowner post-flood reconstruction decisions. It was validated against FEMA damage assessments and post-storm surveys (O’Neil 2017).
Relational integration in schools through seating assignments
Károly Takács Marta Rado | Published Thursday, July 18, 2019We model interpersonal dynamics and study behavior in the classroom in the hypothetical case of a single teacher who defines students’ seating arrangements. The model incorporates the mechanisms of peer influence on study behavior, on attitude formation, and homophilous selection in order to depict the interrelated dynamics of networks, behavior, and attitudes. We compare various seating arrangement scenarios and observe how GPA distribution and level of prejudice changes over time.
Fertility Tradeoffs
Kristin Crouse | Published Tuesday, November 05, 2019 | Last modified Thursday, April 06, 2023Fertility Tradeoffs is a NetLogo model that illustrates the emergencent tradeoffs between the quality and quantity of offspring. Often, we associate high fitness with maximizing the number of offspring. However, under certain circumstances, it pays instead to optimize the number of offspring, having fewer offspring than is possible. When the number of offspring is reduced, more energy can be invested in each offspring, which can have fitness benefits.
Adoption of conservation practices
Irem Daloglu | Published Monday, October 21, 2013This model is designed to investigate the impact of alternative policy approaches and changing land tenure dynamics on farmer adoption of conservation practices intended to increase the water quality.
Model supporting the serious game RÁC
Patrick Taillandier Alexis Drogoul Léo Biré | Published Thursday, January 25, 2024This model is supporting the serious game RÁC (“waste” in Vietnamese), dedicated to foster discussion about solid waste management in a Vietnamese commune in the Bắc Hưng Hải irrigation system.
The model is replicating waste circulation and environmental impact in four fictive villages. During the game, the players take actions and see how their decisions have an impact on the model.
This model was implemented using the GAMA platform, using gaml language.
A double-layer network and the contagion mechanism of China’s financial systemic risk
zou | Published Tuesday, August 13, 2019We establish a double-layer network for China’s financial system, consisting of an interbank lending network and a cross-shareholding network. The loss of diffusion in an interbank lending channel independently, a cross-shareholding channel independently and a double-layer contagion channel after one of the financial institutions goes bankrupt with an initial shock are simulated to explore the nonlinear evolution mechanism of financial risk and impact factors of financial systemic risk in China.
Bayesian Updating Opinion Shared Uncertainty Model.
Johnathan Adams | Published Monday, November 16, 2020 | Last modified Friday, May 14, 2021This is an opinion dynamics model which extends the model found in (Martins 2009). The previous model had an unshared uncertainty assumption in agent-to-agent interaction this model relaxes that assumption. The model only supports a fully connect network where every agent has an equal likelihood of interacting with every other agent at any given time step. The model is highly modular so different social network paradigm can easier be implemented.
Simulating the Cinema Market: How Cross-Cultural Differences in Social Influence Explain Box Office Distributions
Sebastiano Delre | Published Thursday, February 11, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates the motion picture industry and tests how social influences affect market shares. It is empirically validated at the micro level by a cross-cultural survey.
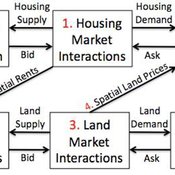
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
Displaying 10 of 1110 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search